Fig. 5. A model of the induction of morphological changes by RNA oxidation in epithelial lung cells exposed to air pollution.
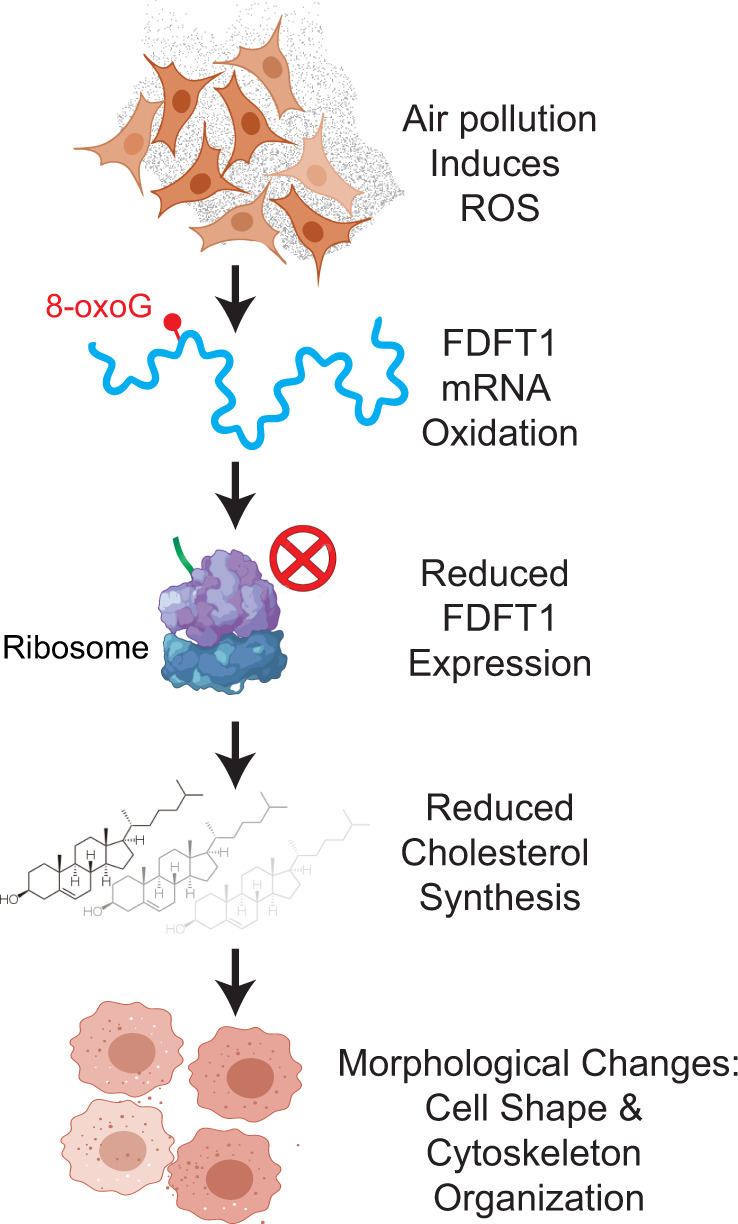
Cells exposed to air pollution experienced increased RNA oxidation as compared with clean air controls. RNA oxidation by air pollution is highly selective as 42 transcripts are consistently oxidized. One of these, FDFT1 is highly enriched in 8-oxoG and significantly downregulated at higher oxidative exposures. This event results in reduced FDFT1 protein levels and lower concentrations of intracellular cholesterol. The FDFT1 knockdown promotes cell morphology changes, including transformation of cell shape and reduction of the cytoskeleton organization. These results provide a model linking FDFT1-mediated cholesterol dysregulation and defects in cellular morphology that emerge post exposure to air pollutants.
