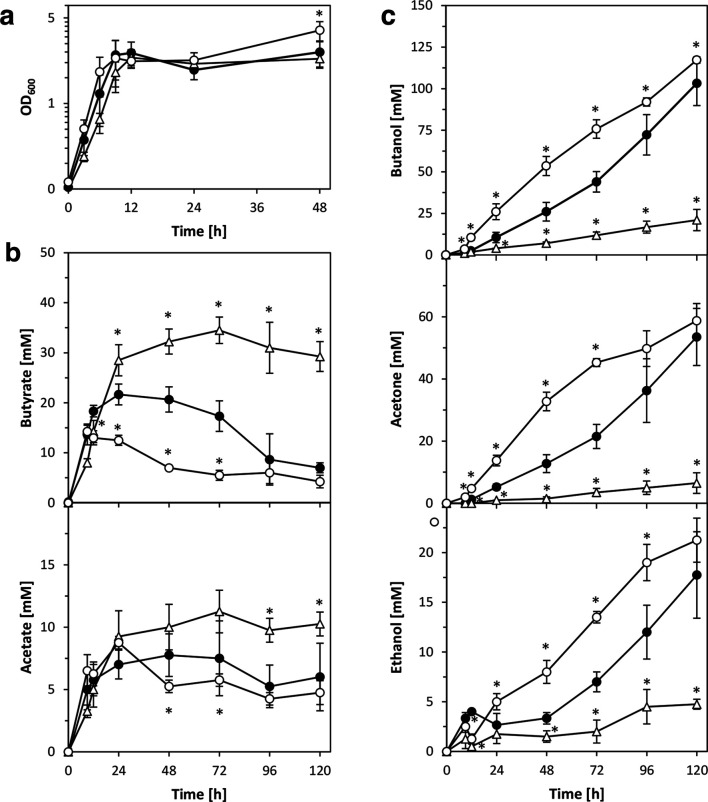
Fig. 2.
Fermentation profile of C. acetobutylicum wild-type, qsrB mutants and genetically complemented qsrB mutants. Growth (a) and production of acids (b) and solvents (c) were compared for the ATCC 824 parent strain containing the empty pMTL85141 vector (closed circles), the qsrB mutants containing the empty pMTL85141 vector (open circles) and the qsrB mutants containing the complementation plasmid pMTL85141-qsrB (open triangles). Data represent the mean of four independent CBMS cultures with error bars indicating the standard deviation. Significant differences (P≤0.05) compared to the wild-type are indicated by an asterisk next to the relevant data point.