Figure 1.
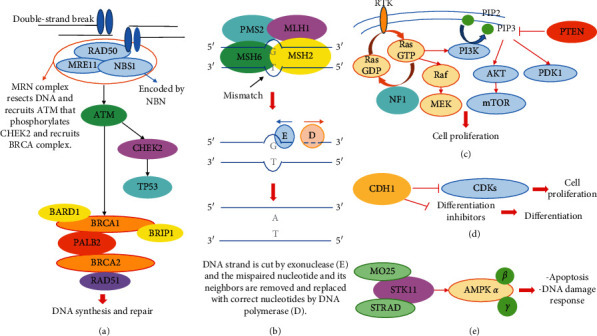
Molecular pathways involved in hereditary cancer risk. Susceptibility genes described in the text are reported in bold. G: guanine, T: thymine, A: adenine, E: exonuclease, D: DNA polymerase, RTK: receptor tyrosine kinase, PIP2: phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, PIP3: phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate, GDP: guanosine diphosphate, GTP: guanosine triphosphate, CDKs; cyclin-dependent kinases, and AMPK: 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. (a) Homologus recombination (HR), (b) mismatch repair (MMR), (c) PTEN and NF1 pathways, (d) CDH1 pathway, and (e) STK11 pathway.
