Figure 3.
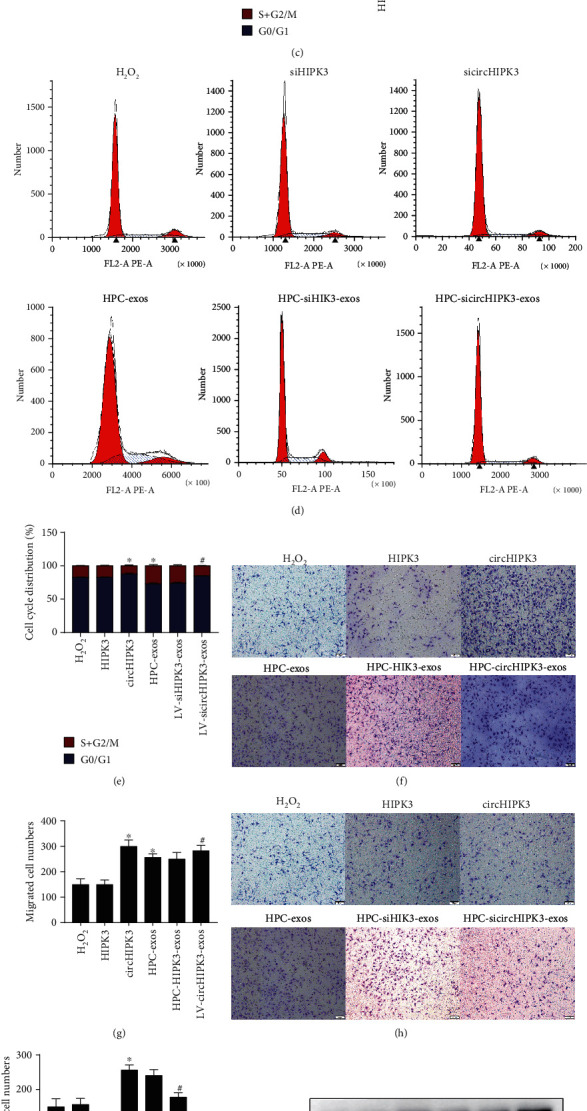
HPC-exosomal circHIPK3 accelerates cell cycle progression and migration of cardiac endothelial cells. circHIPK3, circHIPK3 siRNA, linear HIPK3, or linear HIPK3 siRNA was transfected into cardiac endothelial cells for 48 h to evaluate cell proliferation and migration. Furthermore, cardiac endothelial cells were incubated with HPC-HIPK3-exos, HPC-circHIPK3-exos, HPC-siHIPK3-exos, or HPC-sicircHIPK3-exos to understand the role of exosomal circHIPK3. (a) circHIPK3 expression in cardiac endothelial cells subjected to different treatments was analyzed with qPCR. (b, d) Flow cytometry was performed to analyze the distribution of cells in the cell cycle. (c, e) Representative quantification of the data from (b) and (d), respectively. (f, h) Cell migration among the six groups as confirmed by the Transwell assay (lower, bars = 50 μm). (g, i) The number of migrated cells per field was determined. (j, l) Western blot analyses were performed. (k, m) Quantification of the relative protein levels of cyclinD1 and PCNA in cardiac endothelial cells was performed (means ± SD, n = 3, ∗P < 0.05, compared with the H2O2 group, #P < 0.05 compared with the HPC-exo group).
