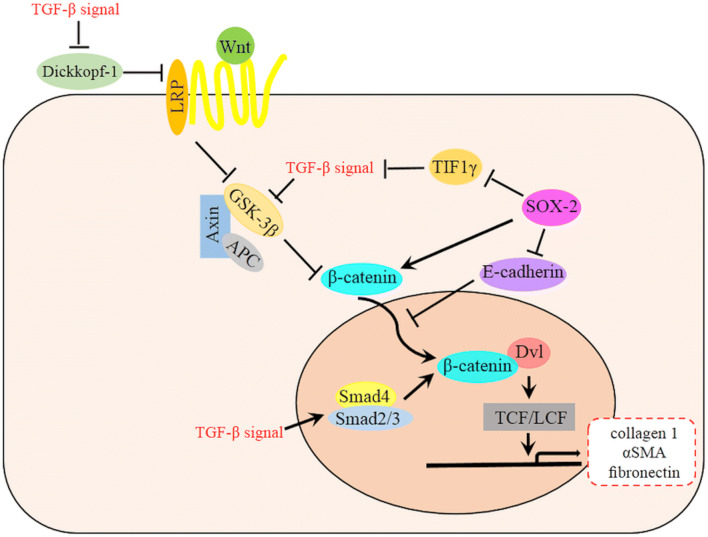
Fig. 1.
A schematic diagram of the relationship between Wnt and TGF-β signaling pathway in EMT. TGF-β signal is involved in many steps of Wnt signaling pathway, which ultimately accumulate β-catenin and then promote the EMT and fibrosis. TGF-β mediates decreased expression of the Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 via a p38-dependent manner while also stimulates Wnt signaling by inhibiting GSK-3β or promoting Smad4 and Smad2/3 complex to increase β-catenin in the cytoplasm and nucleus. TGF-β signal is also activated by SOX2 through the repression of TIF1γ. SOX2 could also promote the Wnt signaling pathway by transcriptional enhancement of β-catenin [46]