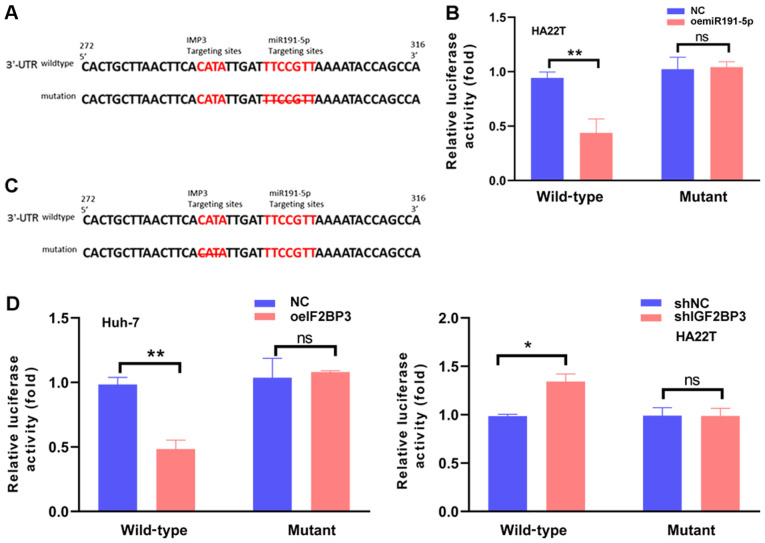
Figure 4.
IGF2BP3 improves miR191-5p-induced silencing complex function by binding the 3′-UTR of ZO-1 mRNA and promoting Ago2-mRNA interactions. (A) Sequence alignment of the ZO-1 3′UTR with wild-type vs. mutant potential miR191-5p targeting sites. The left red sequence represents the potential IGF2BP3 binding site of the ZO-1 mRNA 3′UTR. The right red sequence represents the potential miR191-5p binding site of the ZO-1 mRNA 3′UTR, and the crossed sequence represents deletion in the mutant ZO-1 3′UTR. (B) Luciferase reporter activity after transfection of wild-type and mutant ZO-1 3′UTR reporter constructs in HA22T cells with/without miR191-5p. (C) Sequence alignment of the ZO-1 3′UTR with wild-type vs. mutant potential IGF2BP3 targeting sites. The left red sequence represents the potential IGF2BP3 binding site of ZO-1 mRNA 3′UTR, and the crossed sequence represents deletion in the mutant ZO-1 3′UTR. The right red sequence represents the potential miR191-5p binding site of ZO-1 mRNA 3′UTR. (D) Luciferase reporter activity following transfection with wild-type or mutant ZO-1 3′UTR reporter constructs in Huh-7 cells with/without IGF2BP3-cDNA, and HA22T cells treated with/without IGF2BP3-shRNA, compared with the control cells. All quantifications are presented as the mean ± SD. *P≤0.05 and **P≤0.01. ns, not significant; IGF2BP3/IMP3, insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3; ZO-1, zonula occludens-1; UTR, untranslated region; miR, microRNA; sh, short hairpin (RNA); oe, overexpression; NC, negative control.