Fig. 2.
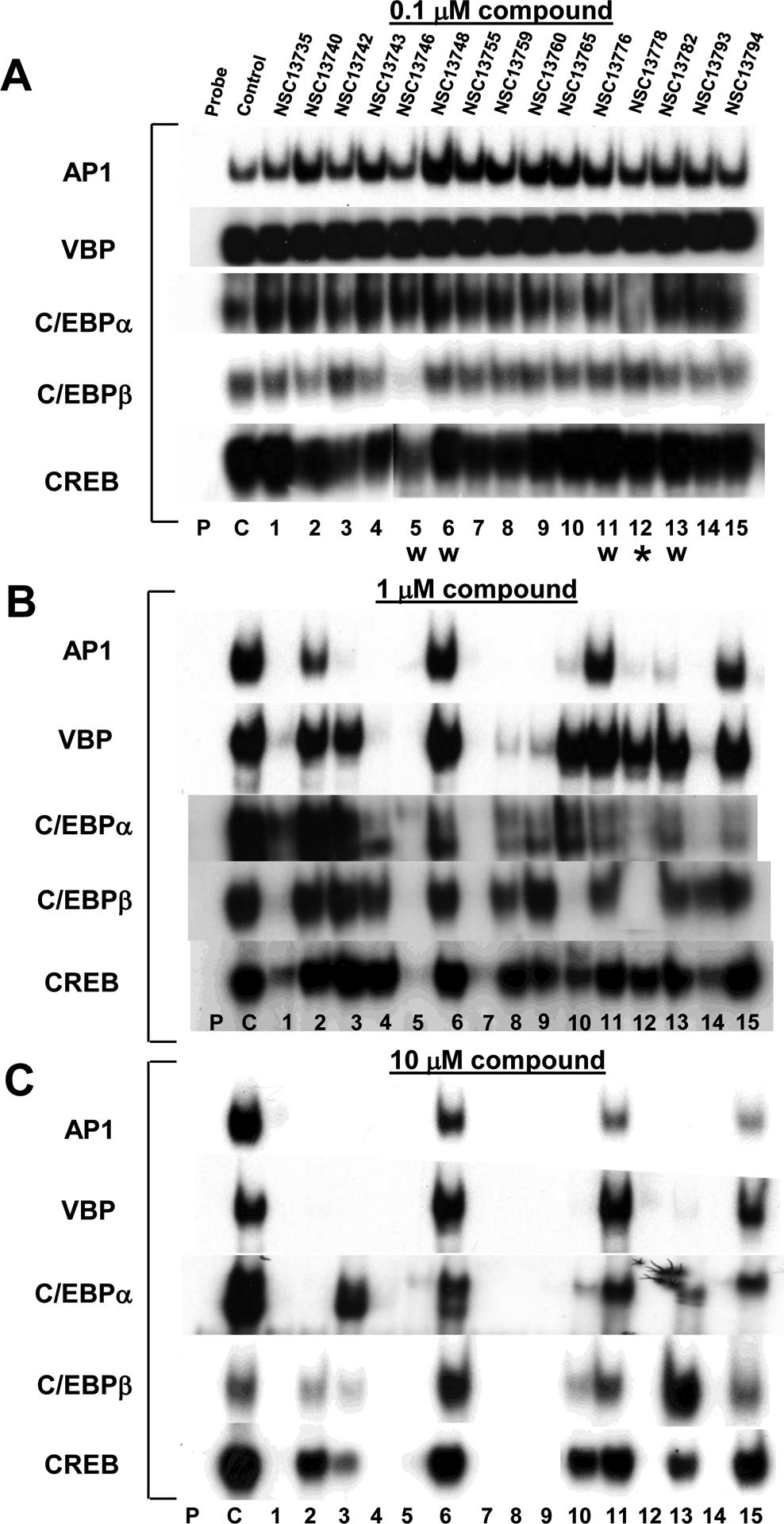
Inhibition of DNA binding of five B-ZIP transcription factors by 15 arylstibonic acids at increasing concentrations. A) EMSA showing the inhibition of DNA binding of AP1 (c-Fos|JunD heterodimer), VBP, C/EBPα, C/EBPβ and CREB by 15 arylstibonic acids at 0.1 μM. Samples contain 10 nM dimer of each protein, 0.1 μM compound, and 7 pM of 28 bp radiolabeled double stranded DNA containing unique binding site for each transcription factor. Probe (P) is radioactive DNA only, control (C) is DNA plus B-ZIP domain and 1–15 contain DNA, protein, and arylstibonic acids identified in Fig. 1. W indicate water-soluble compounds, all other molecules were dissolved in 100 % DMSO. B) Inhibition of B-ZIP DNA binding activity in 1 μM compound. C) Inhibition of B-ZIP DNA binding in 10 μM compound. * identifies NSC13778 described previously [6]. For ease of comparison, only the DNA|B-ZIP complex is shown.
