Fig. 4.
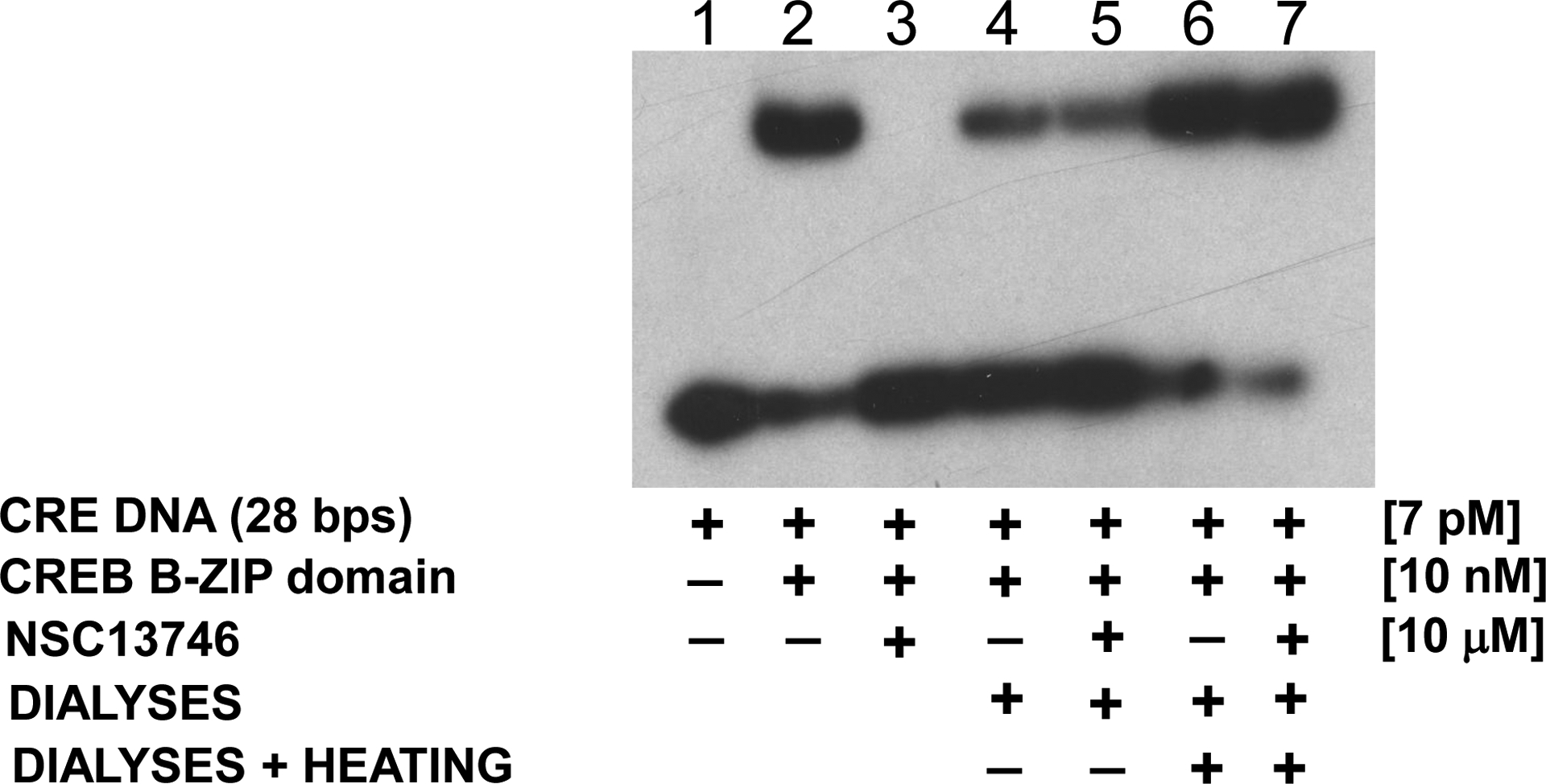
EMSA showing the non-covalent reversible interaction of NSC13746 with the CREB B-ZIP domain. Lanes 2–3 represent protein samples that were not dialyzed whereas samples in lanes 4–7 were dialysed against CD buffer for 24 hour at 4 °C. 1) Radiolabelded double stranded 28 base pair DNA probe containing the consensus CREB binding site. Lane 2) DNA plus 10 nM dimer of the CREB B-ZIP domain produces a DNA|protein complex. Lane 3) DNA, CREB B-ZIP domain, and 10 μM NSC13746. Lane 4) CREB protein sample without NSC13746 was dialyzed overnight against CD buffer (12.5 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, 0.25 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT with 150 mM KCl), mixed with radiolabeled probe and ran on the gel without heating. Lane 5) Sample containing CREB protein with NSC13746 was treated similarly to lane 4. Lane 6) Sample from lane 4 was heated to 50 °C for 5 minutes. Lane 7) Sample from lane 5 was heated to 50 °C for 5 minutes. DNA binding of CREB protein incubated with NSC13746 was completely recovered after dialyses and heat treatment (see text for details) indicating that NSC13746 interact non-covalently and reversibly with CREB protein.
