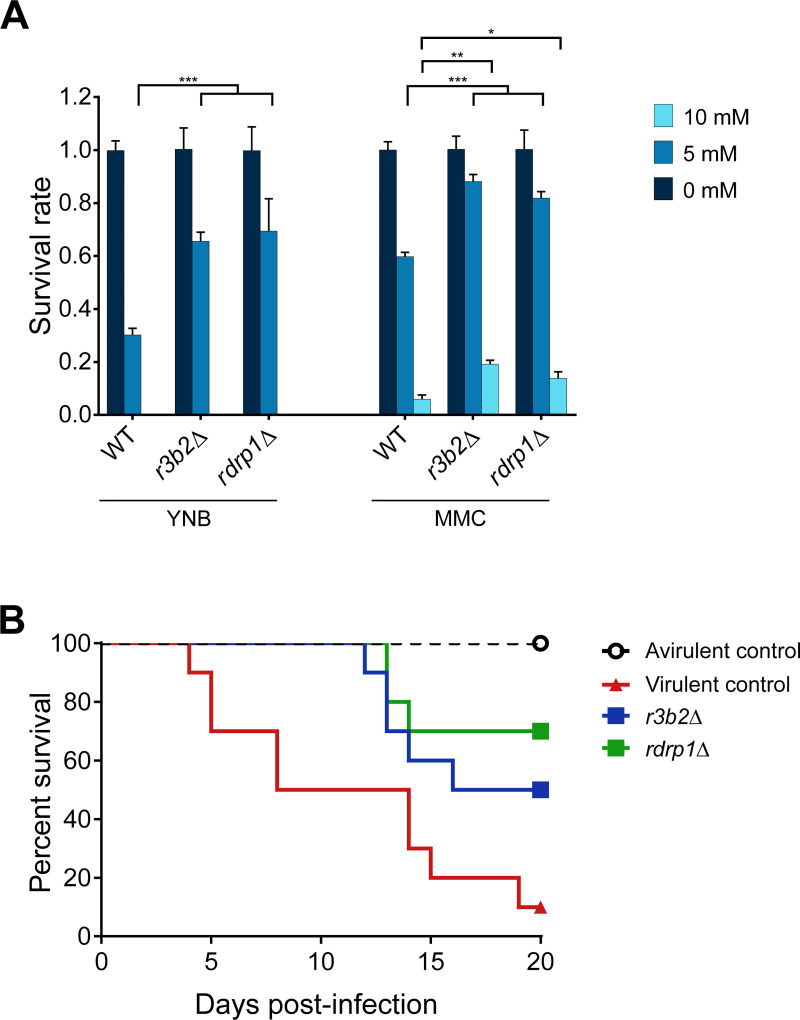
Fig 5. NCRIP is involved in oxidative stress tolerance and mucormycosis.
(A) A bar plot showing the survival rates of the NCRIP mutants (r3b2Δ and rdrp1Δ) compared to a wild-type strain under oxidative stress. Survival assays were performed in two different minimal media (YNB and MMC) supplemented with two different H2O2 concentrations: 5 mM and 10 mM. Error bars correspond to the SD of technical triplicates and significant differences in survival rates were denoted by asterisks (* for P ≤ 0.05, ** for P ≤ 0.005, and *** for P < 0.0001 in a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test). (B) The virulence of r3b2Δ and rdrp1Δ mutant strains was assessed in a survival assay using immunosuppressed mice as a mucormycosis model. Groups of ten mice were infected intravenously with 1x106 spores from each strain (color-coded). Survival rates were statistically analyzed for significant differences (P ≤ 0.05 in a Mantel-Cox test) compared with a virulent control strain (R7B). NRRL3631 was used as an avirulent mock control of infection.