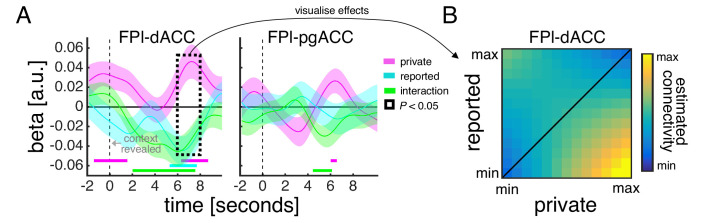
Figure 5. Functional connectivity between medial and lateral prefrontal context varies with contextual requirements of task.
(A) Psychophysiological interaction analysis of ROI activity time courses. Traces are coefficients from a GLM in which we predicted dACC/pgACC activity from the interaction between FPl activity and (1) the model-based estimate of private confidence (pink), (2) the empirically observed confidence reports (cyan) and (3) the interaction between private and reported confidence (green) – while controlling for the main effect of each term. Vertical dashed line indicates the onset of the context screen - the context screen, which is presented for 1 s, is shown .5 s after the submission of the perceptual decision and is immediately followed by the confidence scale. Analyses were performed on trials in which the context was explicitly signalled. We tested significance (coloured square) for each time point by comparing coefficients across subjects to zero (p<0.05, one-sample t-test). (B) Visualisation of FPl-dACC connectivity. Hotter colours indicate greater FPl-dACC connectivity as a function of variation (in z-score units) in private confidence (x-axis) and reported confidence (y-axis). FPl-dACC connectivity was estimated using group-level coefficients averaged across a time window from 6 s to 8 s (box in panel A).