FIGURE 2.
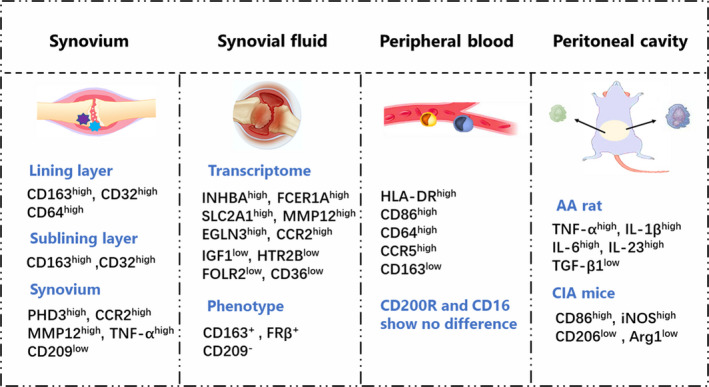
Macrophage polarization in RA. CD163 and CD32 are highly expressed in the synovial lining macrophages of RA patients, CD163, CD32 and CD64 are highly expressed in the macrophages in the lining layer. The synovial macrophages of RA patients highly express MMP12, TNF‐α and the transcription proteins PHD3 and CCR2 of pro‐inflammatory gene EGLN3 and show lower expression of M2 macrophage indicator CD209. RA synovial fluid macrophages express pro‐inflammatory genes (INHBA, FCER1A, SLC2A1, MMP12, EGLN3, CCR2), while express low expression of anti‐inflammatory genes (IGF1, HTR2B, FOLR2, CD36). CD163 and FRβ are expressed in synovial fluid macrophages, while CD209 is not expressed. Some studies confirm that RA synovial fluid highly express M1 macrophage indicators, including HLA‐DR, CD40, CD80, CD86 and CD276. M1 macrophage indicators HLA‐DR, CD86, CD64 and CCR5 are highly expressed in mononuclear macrophages in peripheral blood of RA patients, while M2 macrophage indicators CD163 shows low expression, and CD200R and CD16 show no difference. Peritoneal macrophages from AA rats produce high levels of TNF‐α, IL‐1β, IL‐6 and IL‐23 and low levels of TGF‐β1. Peritoneal macrophages from CIA mice express high levels of CD86 and iNOS and low levels of CD206 and Arg1
