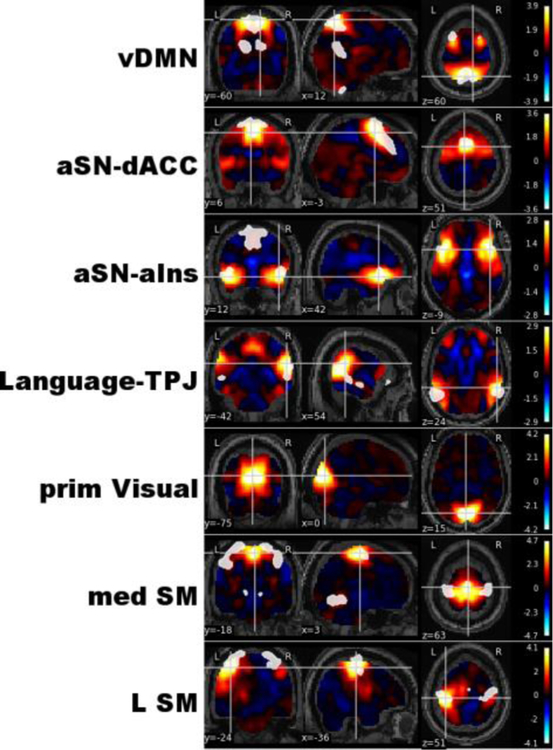
Figure 3.
Intrinsic connectivity networks relevant to autism spectrum disorder. Seven out of 29 intrinsic connectivity networks (ICNs) representing independent processing systems within the brain were associated with autism spectrum disorders. These included the ventral Default Mode Network (vDMN), two subnetworks of the anterior Salience Network centered on the dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex (aSN-dACC) and anterior insula (aSN-aIns), a subnetwork of the Language network centered on the bilateral temporoparietal junction (Language-TPJ), the primary Visual Network (prim Visual), as well as medial and Left Sensorimotor networks (med SM and L SM, respectively). X, Y, and Z coordinates are relative to Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space; weights from independent components analysis (ICA) are displayed in the legend, with binary templates for known ICNs plotted in white (Shirer et al. 2012).