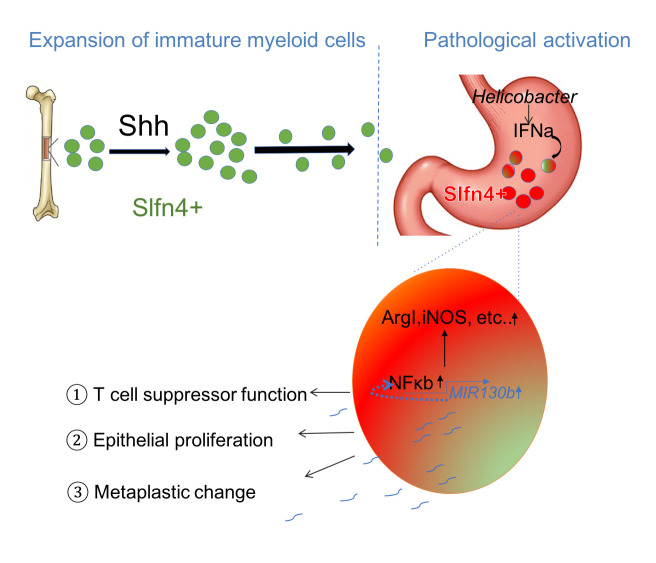
Figure 6.
Schematic of SLFN4+-MDSCs polarised in the stomach during Helicobacter infection. Acute SHH release by parietal cells into the circulation is sensed by BM-derived SLFN4+ myeloid cells (green), which are home to the infected stomach. Eventually, the SLFN4+ myeloid cells become activated and polarised to MDSCs (red) and accumulate in response to tissue IFNα produced during chronic Helicobacter infection. There is a feedback loop between NFκb activation and MIR130b expression in SLFN+-MDSCs (enlarged red cell). MiR130b produced by SLFN+-MDSCs (1) regulate T cell suppressor function, (2) affect epithelial cell proliferation, (3) promote metaplastic changes. MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; SHH, Sonic hedgehog.