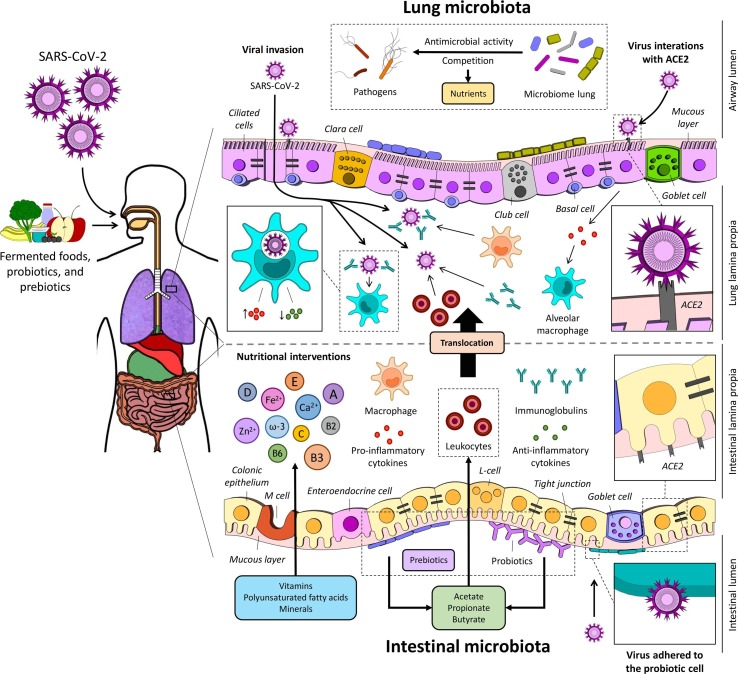
Fig. 2.
Main mechanisms of action of fermented foods, probiotics, and prebiotics. Prebiotics are selectively utilized by the commensal microbiota, releasing metabolites like short chain fatty acids (SCFA), promoting leukocyte recruitment to the site of infection, as well as their activation. The SARS- CoV-2 binds to the ACE2. Fermented foods and probiotics strains may also increase the phagocytic activity and modulate the production of immunoglobulins/antibodies mediate host defense by eliminating intracellular pathogens, improving the immune response, intestinal microbiota has a marked influence on metabolic pathways within alveolar macrophages, which correlates with an altered cellular responsiveness, promoting the microbiota modulation has a marked influence on metabolic pathways within alveolar macrophages, nutritional interventions of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, selenium, zinc, iron, vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, C, D, and E to combat viral infections. ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; L-cell, enteroendocrine L-cell; M cell, microfold cell; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome.