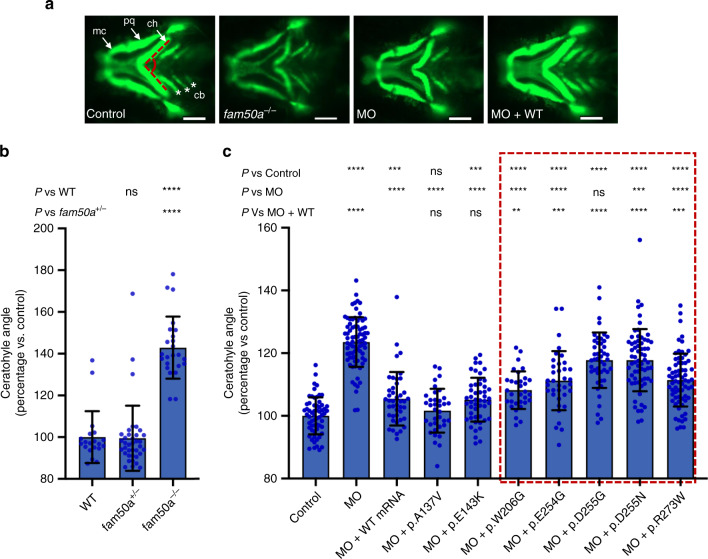
Fig. 3. In vivo assays indicate that FAM50A missense variants confer a partial loss of function.
a Representative ventral views of craniofacial structures imaged live using the VAST BioImager in -1.4col1a1:egfp zebrafish larvae at 3 days post-fertilization (dpf). mc, Meckel’s cartilage; pq, palatoquadrate; ch, ceratohyal arch; cb, ceratobranchial arches. Red dashed lines on control image indicate the ch angle measured to quantify altered cartilage patterning in wild-type (WT) control, KO (homozygous mutants) or morphants. 5 ng morpholino (MO) and/or 150 pg of human FAM50A mRNA were injected for all assays. Scale bars, 100 μm. b Quantification of ch angle in fam50a KO, fam50a+/− (heterozygous mutant) and WT. Heterozygous and WT animals are indistinguishable; ch angle was significantly increased in fam50a KO. **** indicates p < 0.0001. ns, not significant (unpaired Student’s t-test, two-sided). See Supplementary Table 4 for exact p-values. Left to right: n = 20, 37, and 24 larvae per condition, respectively. c In vivo complementation studies indicate that FAM50A variants in XLID males are pathogenic. Quantification of ch angle as indicated by measurements of ventral images (a), and statistical comparison of variant mRNA vs WT mRNA rescue of MO effect indicates that patient-associated variants are hypomorphic (partial loss of function; red dashed box). p.Ala137Val (A136V; rs149558328) and p.Glu143Lys (E143K; rs782017549) are present in hemizygous males in gnomAD and were scored as benign; *, **, ***, **** indicate p < 0.05; 0.01; 0.001; and 0.0001, respectively. ns, not significant (unpaired Student’s t-test, two-sided). Left to right: n = 61, 78, 43, 36, 49, 32, 36, 46, 66, 69 larvae per condition, respectively; replicated. Data are presented as mean values ± standard deviation. See Supplementary Table 4 for exact p-values.