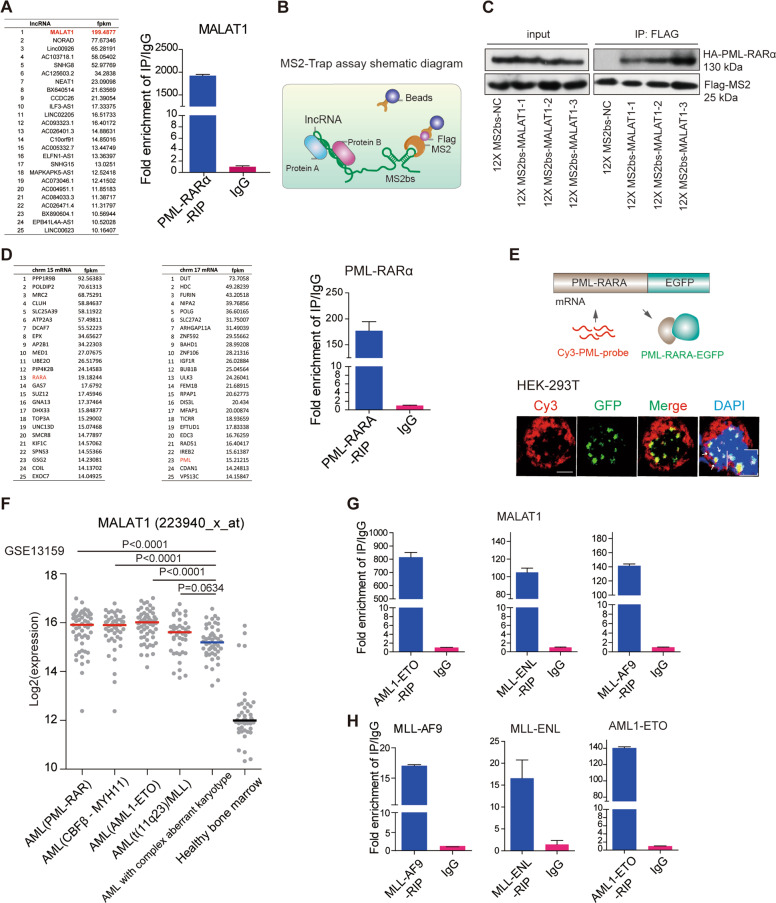
Fig. 1. Both the mRNA and fusion proteins were hijacked in nuclear speckles by MALAT1.
a The mRNAs and lncRNAs binding to PML-RARα (left panel). qRT-PCR validated MALAT1 binding to PML-RARA (right panel). b Schematic diagram showing the procedure of MS2-Trap assays. c PML-RARα interacted with MALAT1 in HEK-293T cells. The three sections of MALAT1 were named as MALAT1-1, MALAT1-2, MALAT1-3 respectively. d The mRNAs binding to PML-RARα. qRT-PCR confirmed the binding (right panel). e The mRNA FISH assay for detecting the interaction of PML-RARα and its own mRNA in HEK-293T cells in which PML-RARα-EGFP over-expressed. PML-RARα-EGFP (green) represents the fusion protein and PML-CY3 (red) represents mRNA transcripts. Scale bar represents 4 μm. f Reanalysis of the GES13159 data set with patient samples classified into many subtypes, including AML with t(11q23)/MLL, AML1-ETO, PML-RAR, and CBFb-MYH11. MALAT1 expression presented the highest levels in the AML patient subgroups with fusion proteins. g, h RIP assays followed by qRT-PCR analysis for the interaction of MALAT1 and the fusion protein mRNAs with fusion proteins (MLL-ENL, AML1-ETO, and MLL-AF9) in HEK-293T cells. Data are shown as the means ± s.e.m.; n = 3 independent experiments.