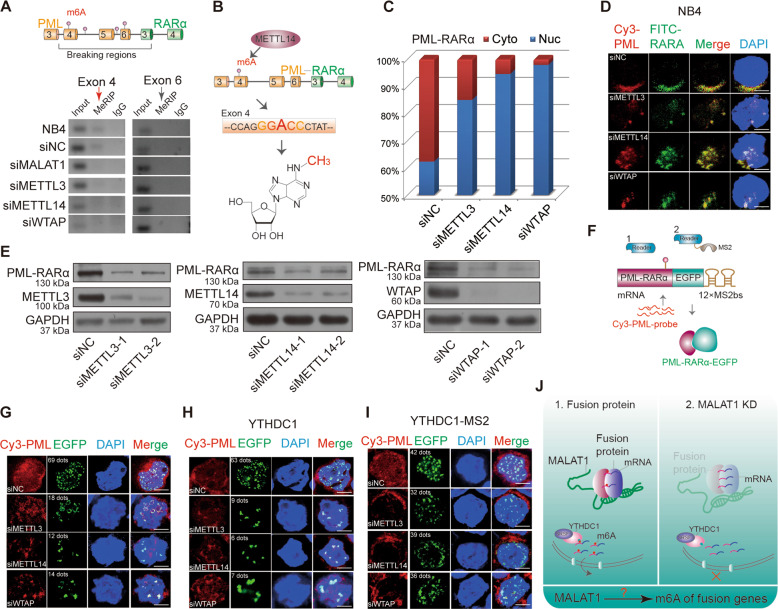
Fig. 4. MALAT1-regulated m6A modification in the nucleus is responsible for the fusion gene export by YTHDC1.
a A schematic showing potential m6A motifs in regions of PML-RARα mRNA. MeRIP assays were performed in NB4 cells after knockdown of m6A methyltransferases, MALAT1 or a negative control with siRNAs. Then, PCR sequencing for these sites, including potential motifs, were carried out; agarose electrophoresis was shown. b Schematic diagram of METTL14-methylated m6A sites in PML-RARα mRNA exon 4. c PML-RARA mRNA dispersion in nuclei and cytoplasm was detected after reducing the m6A level by knocking down the methyltransferases. d RNA FISH analysis showing the PML-RARα mRNA location in cells by two probes, Cy3-PML (red) and FITC-RARα (green). Scale bar represents 4 μm. e The protein levels of PML-RARα, METTL3, METTL14, and WTAP were monitored after knockdown of m6A methyltransferases by several different siRNAs. Three independent experiments were carried out. f Schematic diagram showing RNA FISH assays for testing PML-RARα mRNA transport by transfecting PML-RARα-EGFP-12×MS2bs and YTHDC1-MS2 constructs with knockdown of m6A in HEK-293T cells. g Representative images showed fusion protein green dots were reduced. Red dots were remained in nucleus when m6A methyltransferases were knocked down in HEK-293T cells. Scale bar represents 4 μm. h Combined with cotransfecting YTHDC1 into HEK-293T cells, representative images of PML-RARα mRNA and PML-RARα-EGFP are shown in HEK-293T cells after reducing m6A levels. Scale bar represents 4 μm. i Combined with cotransfecting YTHDC1-MS2, representative images showed PML-RARα mRNA retention in nuclei was significantly restored after reducing m6A, as compared with the negative controls. Scale bar represents 4 μm. j Schematic diagram showing the hypothesis the potential roles of MALAT1, m6A, and the reader YTHDC1 in the fusion gene export process.