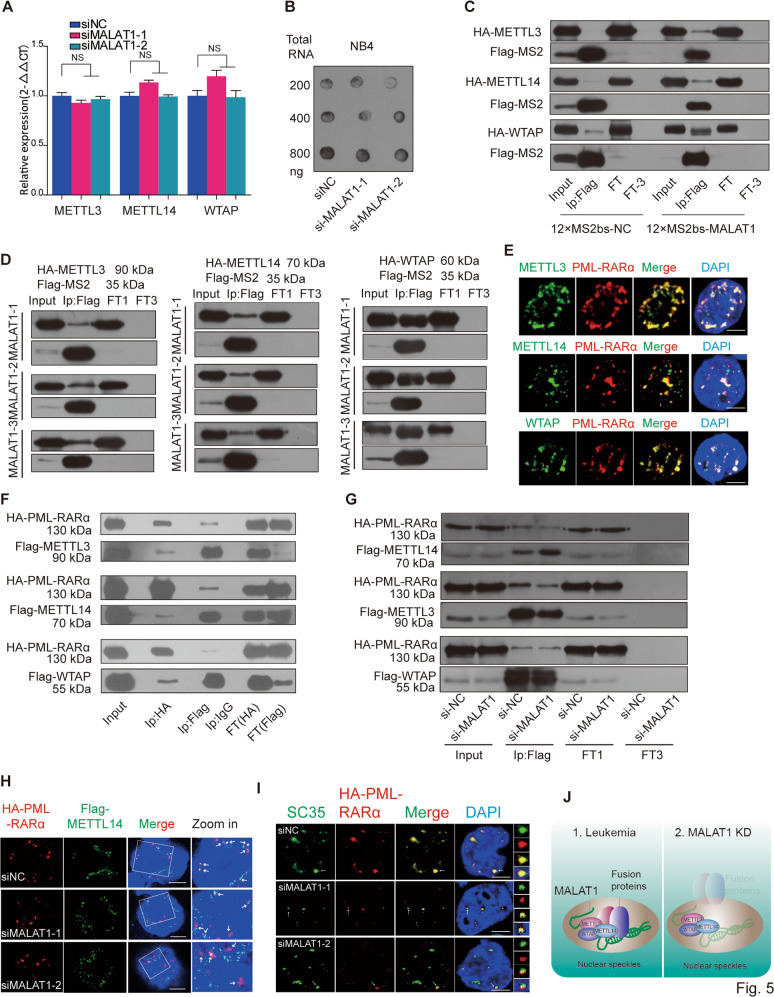
Fig. 5. MALAT1 forms a complex with fusion proteins and m6A methyltransferases.
a m6A methyltransferase expression was not regulated by MALAT1. Data are shown as the means ± s.e.m.; n = 3 independent experiments. b Dot blot assays were performed to determine cellular m6A levels after knockdown of MALAT1. c MALAT1 bound to m6A methyltransferases METTL3, 14 and WTAP directly by MS2-Trap assays in HEK-293T cells (FT1 flow through; FT3 flow through after three times wash).The experiments were performed independently at least three times. d MS2-Trap assays were carried out to test the interactions of METTL3, 14, and WTAP with the three sections of MALAT1. Flow through (FT1) and flow through after washing three times (FT3) were loaded as controls. e Immunofluorescence assays by laser confocal microscopy showed PML-RARα (anti-RARα) and m6A methyltransferases (anti-METTL3, 14, and WTAP) co-localized in NB4 cells. Scale bar represents 4 μm. f Co-immunoprecipitation and Western blot experiments were used to further detect the interaction of PML-RARα and m6A methyltransferases in HEK-293T cells (FT1 flow through; FT3 flow through after three times wash). g Co-immunoprecipitation of HA-tagged PML-RARA with Flag-tagged METTL3, 14, and WTAP in HEK-293T cells with MALAT1 knockdown by siRNA. Flow through (FT1) and flow through after washing three times (FT3) samples were loaded as controls. h HA-PML-RARα (anti-HA) and Flag-METTL14 (anti-Flag) localized in different positions in nuclei following knockdown of MALAT1 in HEK-293T cells by the methods of immunofluorescence. Scale bar represents 4 μm. i The nuclear localization of HA-PML-RARα (anti-HA) and nuclear speckle marker SC35 (anti-SC35) was only partially overlapping in the siMALAT1 samples compared to the negative controls in immunofluorescence assays. Representative images from confocal microscopy are shown from three independent experiments, scale bar represents 4 μm. j Schematic models indicating the potential mechanistic roles of fusion proteins and m6A methyltransferases in nuclear speckles.