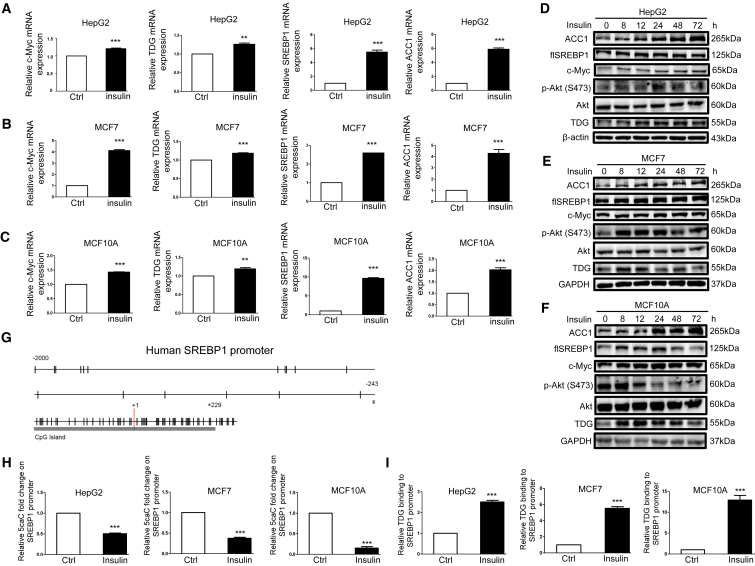
Figure 1.
Insulin Upregulates c-Myc, TDG, SREBP1, and ACC1 Expression; Lowers 5caC Abundance in the SREBP1 Promoter; and Increases TDG Binding to the SREBP1 Promoter
(A and D) HepG2 cells, (B and E) MCF7 cells, and (C and F) MCF10A cells were treated with 200 nM insulin for 48 h (A–C) or for indicated time periods (D–F). Relative c-Myc, TDG, SREBP1, and ACC1 mRNA, determined via qRT-PCR, was shown as the mean plus SEM of a representative experiment performed in triplicates. ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student’s t test). Cell lysates were analyzed by western blot with specified antibodies. flSREBP1, full-length SREBP1. (G) Schematic representation of the CpG distribution in the upstream of 2,000 bp from the transcription start site (+1) and exon 1 of the SREBP1 gene. The CpG sites are represented by vertical tick marks, and the CpG island predicted by MethPrimer is labeled. (H) Relative 5caC abundance in the SREBP1 promoter upon 200 nM insulin treatment for 48 h was detected by the DIP assay using the 5caC antibody followed by qPCR with specific primers in HepG2, MCF7, and MCF10A cells. (I) The relative amount of TDG binding to the SREBP1 promoter upon 200 nM insulin treatment for 48 h was analyzed by the ChIP assay using the TDG antibody followed by qPCR with specific primers in HepG2, MCF7, and MCF10A cells. Fold enhancement represented the abundance of enriched DNA fragments over an IgG control, and the number was shown as the mean plus SEM of a representative experiment performed in triplicates. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student’s t test).