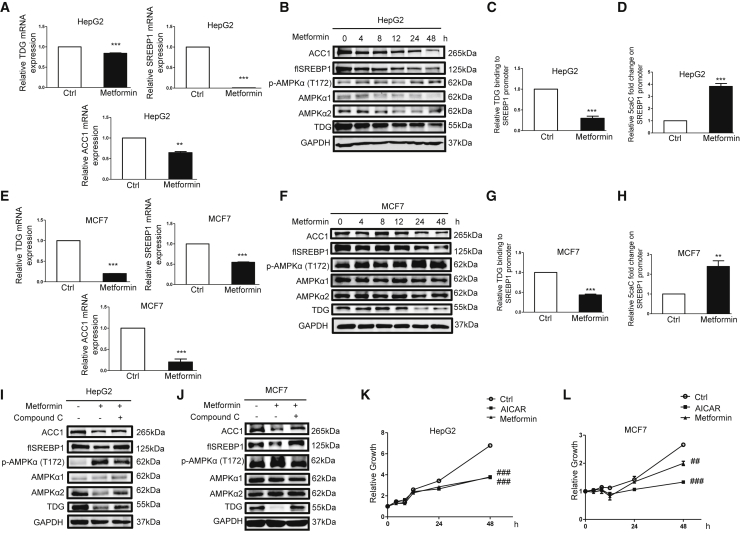
Figure 5.
Activation of AMPK by Metformin Reduces TDG, SREBP1, and ACC1 Expression; Lowers TDG Binding to the SREBP1 Promoter; and Increases 5caC Abundance in the SREBP1 Promoter
(A–D) HepG2 cells were treated with 10 mM metformin for 48 h (A, C, and D) or indicated time periods (B). (E–H) MCF7 cells were treated with 10 mM metformin for 48 h (E, G, and H) or indicated time periods (F). Relative TDG, SREBP1, and ACC1 mRNA, determined via qRT-PCR, were shown as the mean plus SEM of a representative experiment performed in triplicates. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blot with specified antibodies. flSREBP1, full-length SREBP1. The relative amount of TDG binding to the SREBP1 promoter was analyzed by the ChIP assay. Relative 5caC abundance in the SREBP1 promoter was detected by the DIP assay. ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student’s t test). (I and J) HepG2 (I) or MCF7 (J) cells were treated with 5 μM or 1 μM AMPK inhibitor compound C for 30 min prior to 10 mM metformin treatment for 48 h, respectively. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blot with specified antibodies. (K and L) HepG2 (K) or MCF7 (L) cells were treated with 10 mM metformin or 1 mM AICAR for indicated time periods. Cell growth was measured by MTT assay and shown as the mean plus SEM of a representative experiment performed in triplicates. Comparisons of growth curves were analyzed by the mixed regression model, and ##p < 0.01 and ###p < 0.001 were considered to be statistically significant.