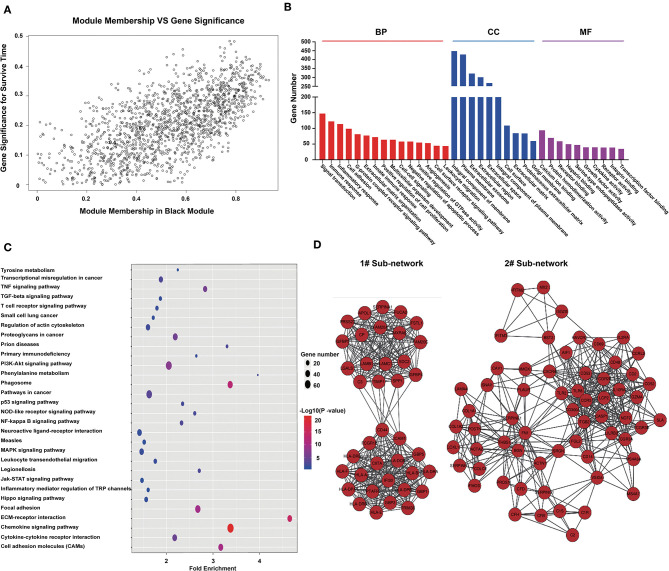
Figure 2.
Genes in the black module are involved in immune responses and the formation of extracellular matrix. (A) Scatterplot of gene significance for survival time (y-axis) vs. module membership (x-axis) in the black module. The correlation coefficient between them is 0.64 (p-value:1.1e-175). (B) Histogram of GO analysis for all genes in the black module. MF, CC, and BF respectively represent molecular function, biological process, and cellular component. The FDR values of the corresponding MF items are: 5.71E-07, 1.06E-36, 9.25E-36, 0.089116, 1.8E-18, 0.007131, 6.21E-32, 4.83E-07, 0.007879, 0.001471, 9.37E-11, 2.63E-11, 2.43E-10, 0.002713, and 0.000293; CC items: 1.25E-21, 3.71E-32, 1.72E-07, 8.90E-24, 4.61E-07, 4.83E-14, 6.92E-06, 5.71E-17, 3.35E-11, and 2.63E-06; BF items: 5.64E-05, 7.84E-04, 7.04E-06, 1.82E-15, 1.51E-05, 30E-08, 1.75E-06, 6.34E-04, 0.001701, and 2.39E-09. (C) Bubble chart of KEGG pathway analysis for all genes in the black module. (D) Protein–protein network constructed by all genes in the black module. Genes were divided into some subnets based on degree of connection. The figure shows the two largest subnetworks. Most of the genes in these subnets are involved in immune responses and the formation of extracellular matrix.