Figure 3.
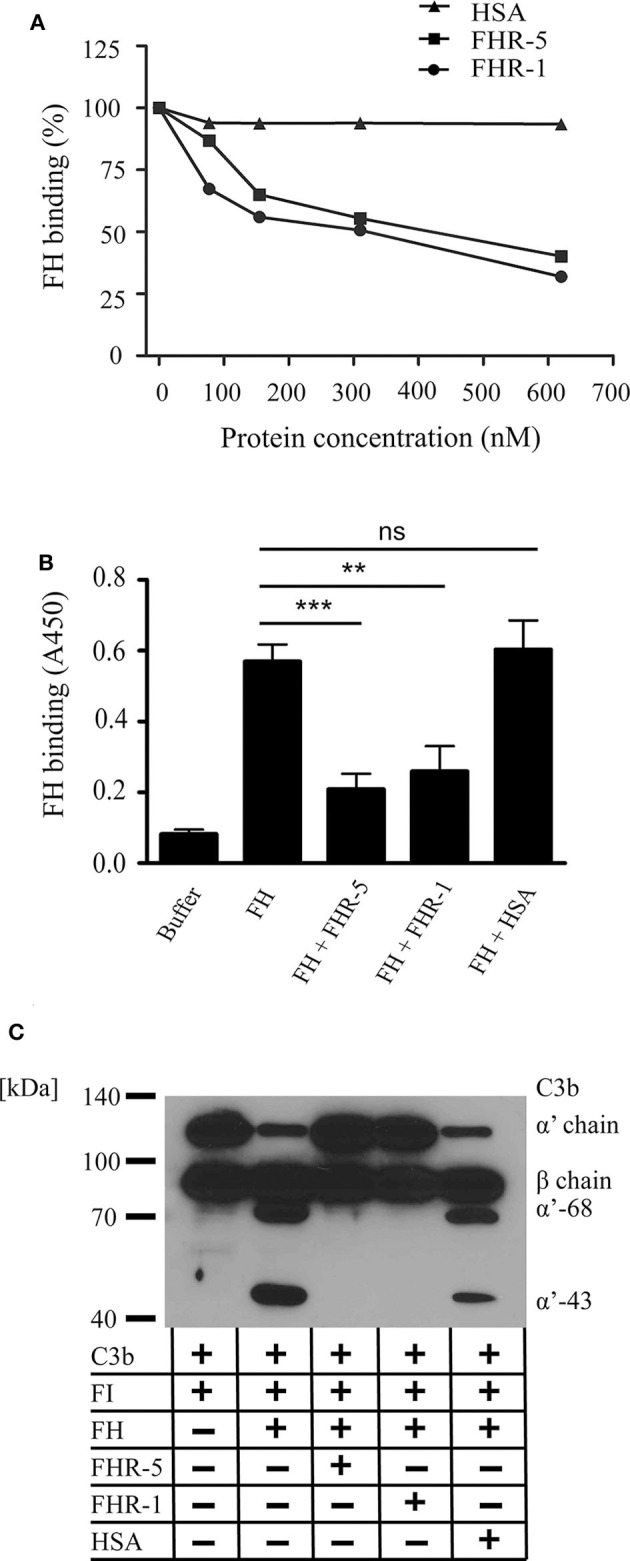
FHR-5 and FHR-1 compete with FH on gDNA and reduce FH cofactor activity. (A) FHR-5 and FHR-1 dose-dependently inhibit FH binding to gDNA. FH (100 nM) was added to immobilized gDNA in the presence of increasing concentrations of FHR-5, FHR-1, or HSA. FH binding was detected with the FH-specific mAb A254 that does not recognize FHR-5 or FHR-1. A representative experiment is shown. (B) Inhibition experiments were repeated at 300 nM FHR-5 and FHR-1. Data are means ± SD derived from four independent experiments. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns, not significant, one-way ANOVA. (C) Analysis of the cofactor activity of DNA-bound FH in the presence of FHR-1 or FHR-5. gDNA was immobilized, 100 nM FH was added alone or in the presence of 300 nM FHR-5, FHR-1, or HSA as negative control. After washing, C3b and FI were added, and the plate was incubated at 37°C for 60 min. Supernatants were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blot for C3b cleavage products under reducing conditions. Inhibition of FH binding to gDNA by FHR-1 and FHR-5 resulted in loss of C3b cleavage. A representative blot from three independent experiments is shown.
