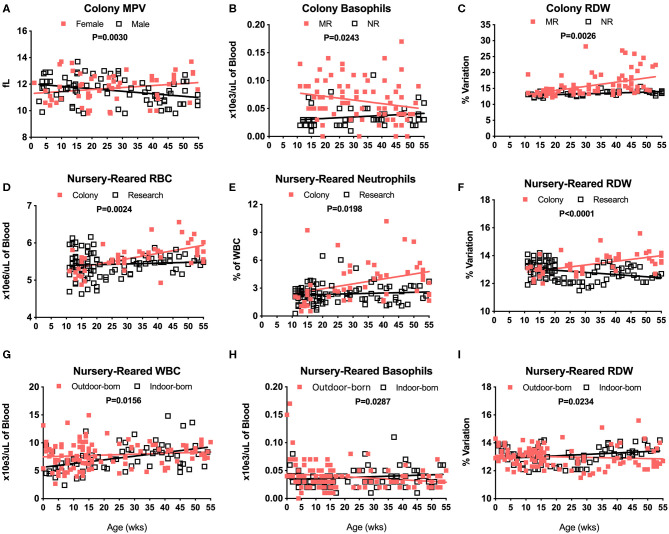
Figure 3.
Relationships were assessed between selected CBC values and groups of colony and nursery-reared pediatric animals over age at time of specimen collection. Linear regression and ANCOVA were performed to compare slopes between male and female colony animal MPV data for increasing age (Male: slope = −0.0188, R2 = 0.1016; Female: slope = 0.015, R2 = 0.0434) (A) and in Colony MR and Colony NR animals over age for number of basophils (MR: slope = 0.0006, R2 = 0.0518; NR: slope = 0.0003, R2 = 0.0382) (B) and RDW (MR: slope = 0.0282, R2 = 0.2117; NR: slope = 0.0269, R2 = 0.2931) (C). Linear regression comparisons via ANCOVA between Colony NR and Research NR animals over age were plotted for RBC count (Colony: slope = 0.0146, R2 = 0.3454; Research: slope = 0.0021, R2 = 0.0072) (D), neutrophil numbers (Colony: slope = 0.0531, R2 = 0.1205; Research: slope = 0.0076, R2 = 0.0092) (E), and RDW (Colony: slope = 0.0269, R2 = 0.2931; Research: slope = −0.0156, R2 = 0.0992) (F). Linear regressions and ANCOVA comparing NR animals born outdoors vs. indoors were shown for WBC numbers (Outdoor: slope = 0.0156, R2 = 0.0144; Indoor: slope = 0.0661, R2 = 0.1888) (G), basophil numbers (Outdoor: slope = −0.0003, R2 = 0.0384; Indoor: slope = 0.0002, R2 = 0.0233) (H), and RDW (Outdoor: slope = −0.0043, R2 = 0.0099; Indoor: slope = 0.0105, R2 = 0.0681) (I).