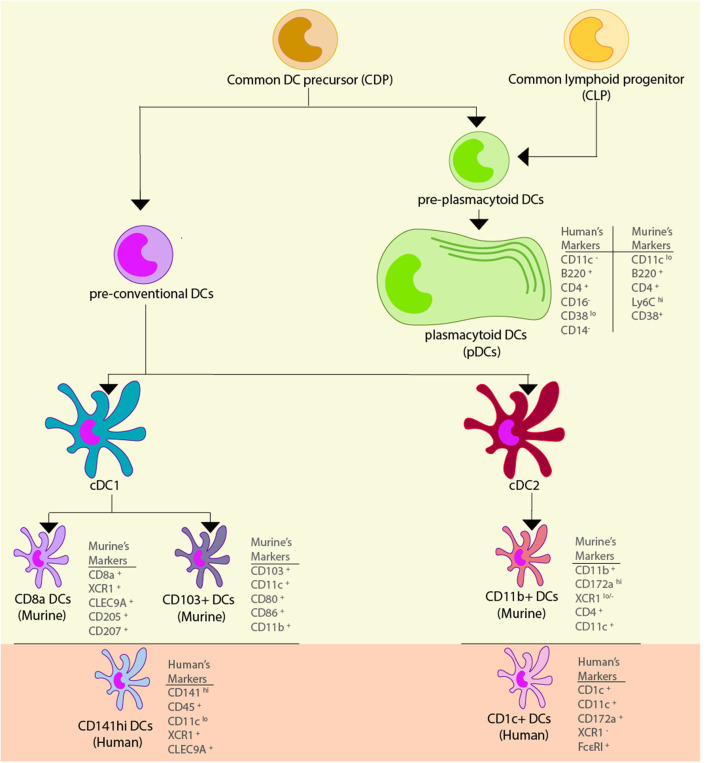
Figure 1.
Dendritic cell subsets. Dendritic cells (DCs) are derived from a common myeloid precursor, from which two precursors can be developed. The first precursor corresponds to the pre-conventional DCs and in murine models they can become conventional DCs (cDCs) type 1 and 2, and within these cells there are different subtypes of DCs. In the cDC1 found two subtypes of cells can be found: CD8+ DCs which has the markers CD8+, XCR1+, CLEC9A+, CD205+, and CD207+, and CD103+ DCs that has the markers CD103+, CD11c+, CD80+, CD86+, and CD11b+. The functional homolog of these cells in human are the CD141hi DCs, and their markers correspond to CD141hi, CD45+, CD11clo, XCR1+, and CLEC9A+. In the cDC2 subsets are comprised the CD11b+ DCs which has the markers CD11b+, CD172ahi, XCR1lo/−, CD4+, and CD11c+. The functional homolog of these cells in human are the CD1c+ DCs, and their markers are CD1c+, CD11c+, CD172a+, XCR1−, and FcεRI+. The second precursor corresponds to the pre-plasmacytoid DCs that can become plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), and in murine models its markers correspond to CD11lo, B220+, CD4+, Ly6Chi, and CD38+, while in human, their markers correspond to CD11−, B220+, CD4+, CD11a+, and CD38lo.