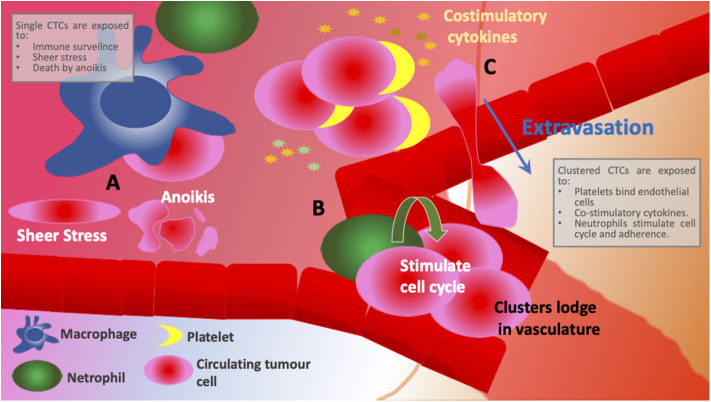
Figure 2.
Schematic comparing different environments encountered between individual CTCs and clusters. (A) Individual CTCs are exposed to immune surveillance, shear stress and have low levels of adhesion and, therefore, open to cell death by anoikis. (B) CTC clusters are supported by neutrophil integration that induces cell cycle progression and DNA replication in CTCs. Larger cellular clusters are more likely to get entrapped in narrow vasculature promoting remodeling and secondary site growth. (C) Platelets interact with endothelial cells and anchor CTCs to the site of extravasation resulting not only in more efficient colonization at new sites but also in less time spent in circulation. CTC clusters provide co-stimulatory cytokines as well as corresponding cytokine receptors, evidence of immune reprogramming and active signaling.