Figure 6.
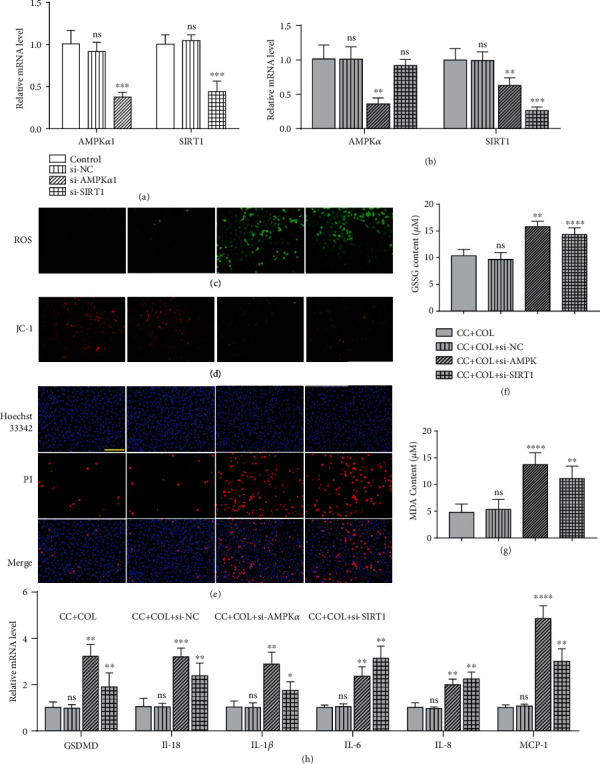
Silencing of AMPK-SIRT1 signaling eliminates the protective effect of colchicine on endothelial cells. HUVECs were transfected with siRNA targeting AMPα1 (si-AMPKα1) and SIRT1 (si-SIRT1) or a control siRNA (Si NC) or were not transfected (-). Cells were then added to cholesterol crystal (0.5 mg/ml) in the presence of colchicine (10 nM) for 10 or 24 hrs. Real-time PCR analysis of the mRNA expression of AMPKα and SIRT1 after transfection with si-AMPKα1, si-SIRT1, and si-NC for 24 hrs without (a) or with (b) the presence of cholesterol crystals and colchicine. (c) Intracellular ROS level was detected using a DCFH-DA probe, and (d) mitochondrial membrane potential was tested by JC-1. (e) Pyroptotic cell death was measured with Hoechst 33342 (blue)/PI (red) double-fluorescent staining. (f, g) The indicators of oxidative stress GSSG and MDA were tested by assay kits. (h) Real-time PCR analysis of the mRNA levels of GSDMD and proinflammatory cytokines (IL-18, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1). Scale bars = 100 μm. Data was expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 vs. the si-NC group or CC+COL+si-NC group.
