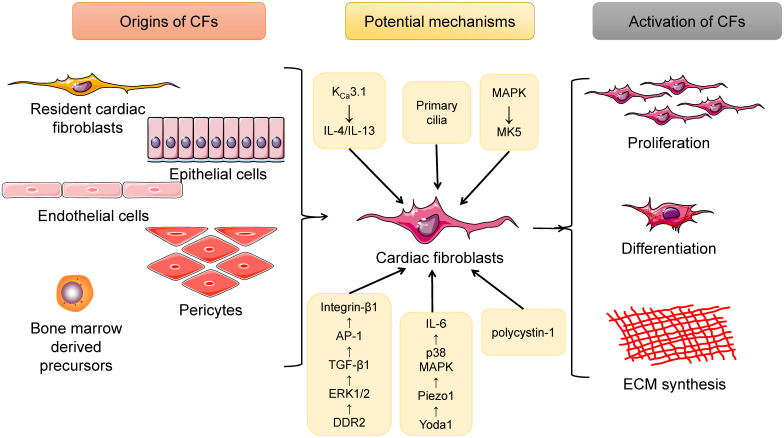
Figure 1.
Summary of the origins as well as the activation of cardiac fibroblasts (CFs). CFs have several sources, including resident cardiac fibroblasts, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, pericytes, and bone marrow-derived cells. When exposed to pressure/volume-overload or other pathological stimuli, CFs will undergo proliferation as well as differentiation into myofibroblasts, cells that can produce large amounts of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins and directly contribute to cardiac fibrosis. In addition, a lot of potential mechanisms are involved in this process.