Table 4.
Summary of the most important compounds identified as allosteric modulators of HSP90.
| Name | Structure | Pharmacokinetics | Mechanism | Residues | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Novo biocin | 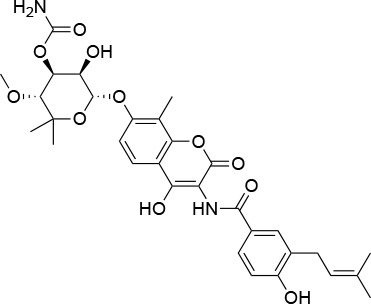 |
IC50 (SkBr3) ~700 μMa | Disruption of the interaction with the co-chaperones Hsc70 and p23 | L663—H676 | (140–142) |
| Chloro biocin | 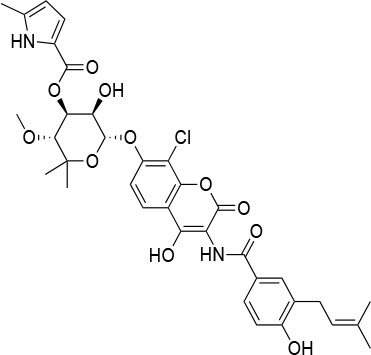 |
IC50 (SkBr3) ~60 μMa | Unknown | Unknown | (141, 142) |
| 15a | 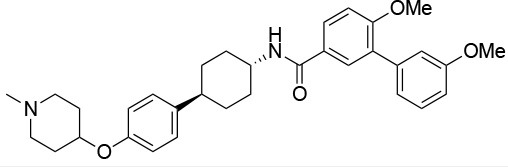 |
IC50 (SkBr3) ~0.17 ± 0.02 μMb IC50 (MCF-7) ~0.22 ± 0.01 μMb |
Unknown | Unknown | (143) |
| 80c | 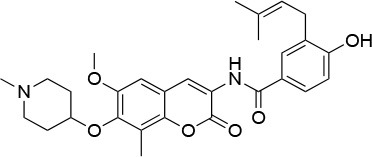 |
IC50 (SkBr3) ~0.42 ± 0.01 μMb IC50 (MCF-7) ~0.54 ± 0.02 μMb |
Unknown | Unknown | (144) |
| Derrubone | 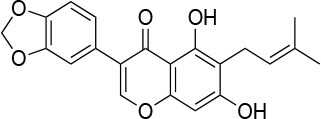 |
IC50
~ 0.23 ± 0.04 μMc IC50 (SkBr3) ~12 ± 0.3 μMb IC50 (MCF-7) ~9 ± 0.7 μMb |
Stabilization of HSP90-client interactions | Unknown | (145) |
| Withaferin A | 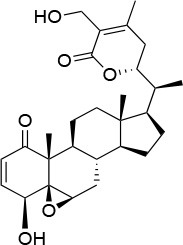 |
IC50 (Panc-1) ~1.24 μMb IC50 (MiaPaCa2) ~2.78 μMb |
Disruption of the HSP90-Cdc37 complex in an ATP-independent way | Unknown | (146) |
| Celastrol | 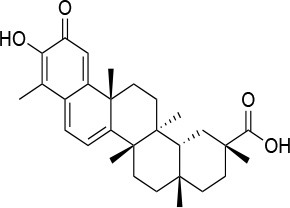 |
IC50 (Panc-1) ~3 μMb IC50 (Hep3B) ~0.3 ± 0.08 μMb |
Disruption of the association between HSP90 and Cdc37 | T94 – M125 | (147, 148) |
| 19 | 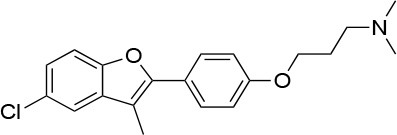 |
IC50 (DU145) ~12.7 ± 2.5 μMb IC50 (STO) ~9.1 ± 1.1 μMb |
Acceleration of the HSP90 conformational cycle | E477, D503 (protomer A), R591 (protomer B) | (149) |
| 25 | 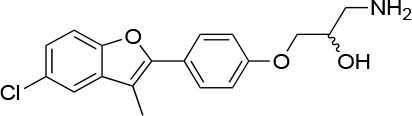 |
IC50 (STO) ~22.1 ± 1.1 μMb | Increased HSP90 ATPase activity favoring its active state | E477, R591 (protomer A), K594 (protomer B) | (150) |
| LA1011 | 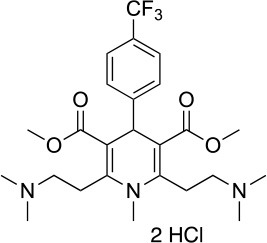 |
Kd (HSP90α) ~3.8 ± 0.7 μMd Kd (HSP90β) ~9.7 ± 0.7 μMd |
Alteration of HSP90 chaperoning activity | G675, S677, L678 | (151) |
Expression levels of HSP90 client proteins.
Anti-proliferation assay.
Luciferase refolding.
Isothermal titration calorimetry.
