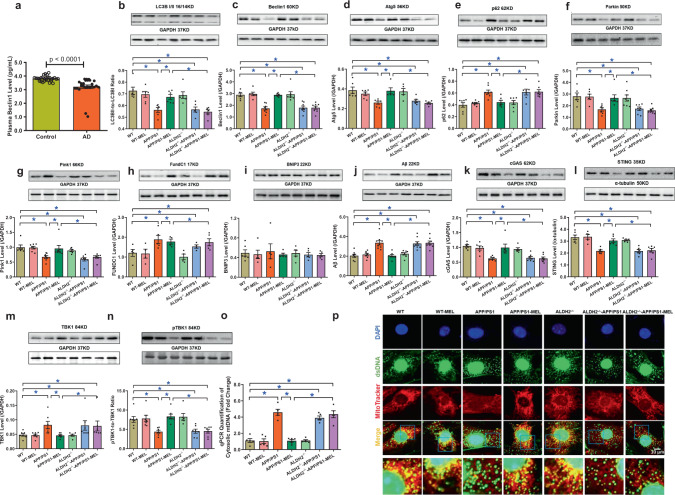
Fig. 7.
Circulating Beclin1 levels in Alzheimer’s disease patients (n = 28) and age-matched controls (n = 25), and the effect of melatonin (20 mg/kg/day, p.o., 6 weeks) on autophagy and mitophagy levels in WT, APP/PS1, ALDH2-knockout (ALDH2−/−), and ALDH2−/−-APP/PS1 mice. a Circulating Beclin1 level; b LC3BII to I ratio; c Beclin1 level; d Atg5 level; e p62 level; f Parkin level; g Pink1 level; h FundC1 level; i Bnip3 level; j Aβ level; k cGAS level; l STING level; m TBK1 level; n phosphor-TBK1 level; o qPCR assessment of in vivo cytosolic mtDNA levels from adult mouse hearts; and p representative immunocytochemistry images of cytosolic DNA accumulation in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes from WT, APP/PS1, ALDH2 knockout (ALDH2−/−), and ALDH2−/−-APP/PS1 neonates treated with or without melatonin (Mel, 100 μΜ) for 4 h prior to assessing mtDNA using a dsDNA antibody and MitoTracker. mtDNA (dsDNA colocalized with MitoTracker, yellow dots), nuclear DNA (dsDNA in the nucleus colocalized with DAPI), and cytosolic DNA (dsDNA not colocalized with mitochondria or the nucleus, green dots) are presented. APP/PS1 mutation promotes buildup of cytosolic dsDNA, which was mitigated by melatonin treatment, whereas ALDH2 ablation abrogated the beneficial effect of melatonin, n = 4 biological repeats for p. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM, n = 5–9 mice per group. *p < 0.05 between the indicated groups