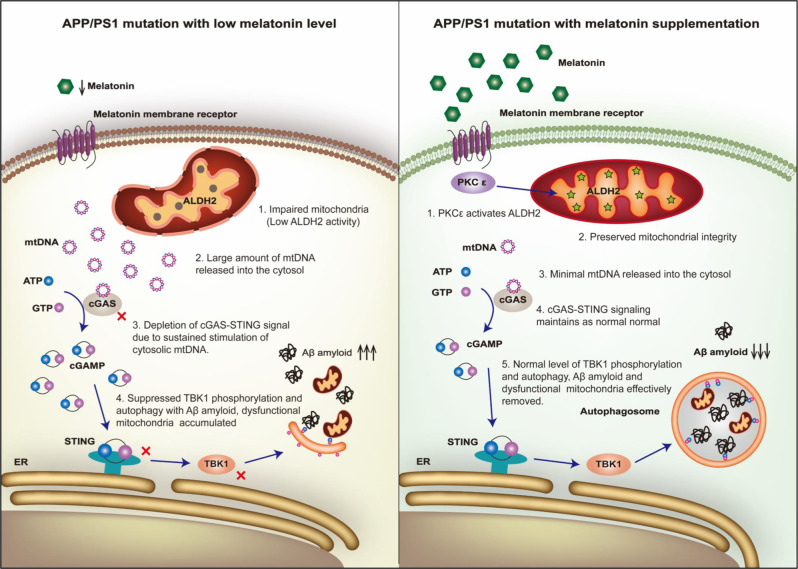
Fig. 9.
Melatonin protects against AD-associated heart dysfunction through ALDH2 and cGAS-STING-TBK1 signaling. AD is associated with decreased melatonin levels, which leads to suppressed ALDH2 activity. Impaired activity of the mitochondrial protein ALDH2 results in damage to mitochondrial integrity, causing mtDNA to be released into the cytosol. A large amount of mtDNA depletes cGAS-STING-TBK1 signaling, leading to suppressed levels of autophagy and mitophagy. These responses further impair clearance of Aβ and mitochondria, ultimately resulting in heart dysfunction. Melatonin supplementation protects heart function in AD by boosting ALDH2 activity through PKCε, thus restoring mitochondrial integrity, cGAS-STING-TBK1 signaling, and autophagy and mitophagy levels