Figure 3.
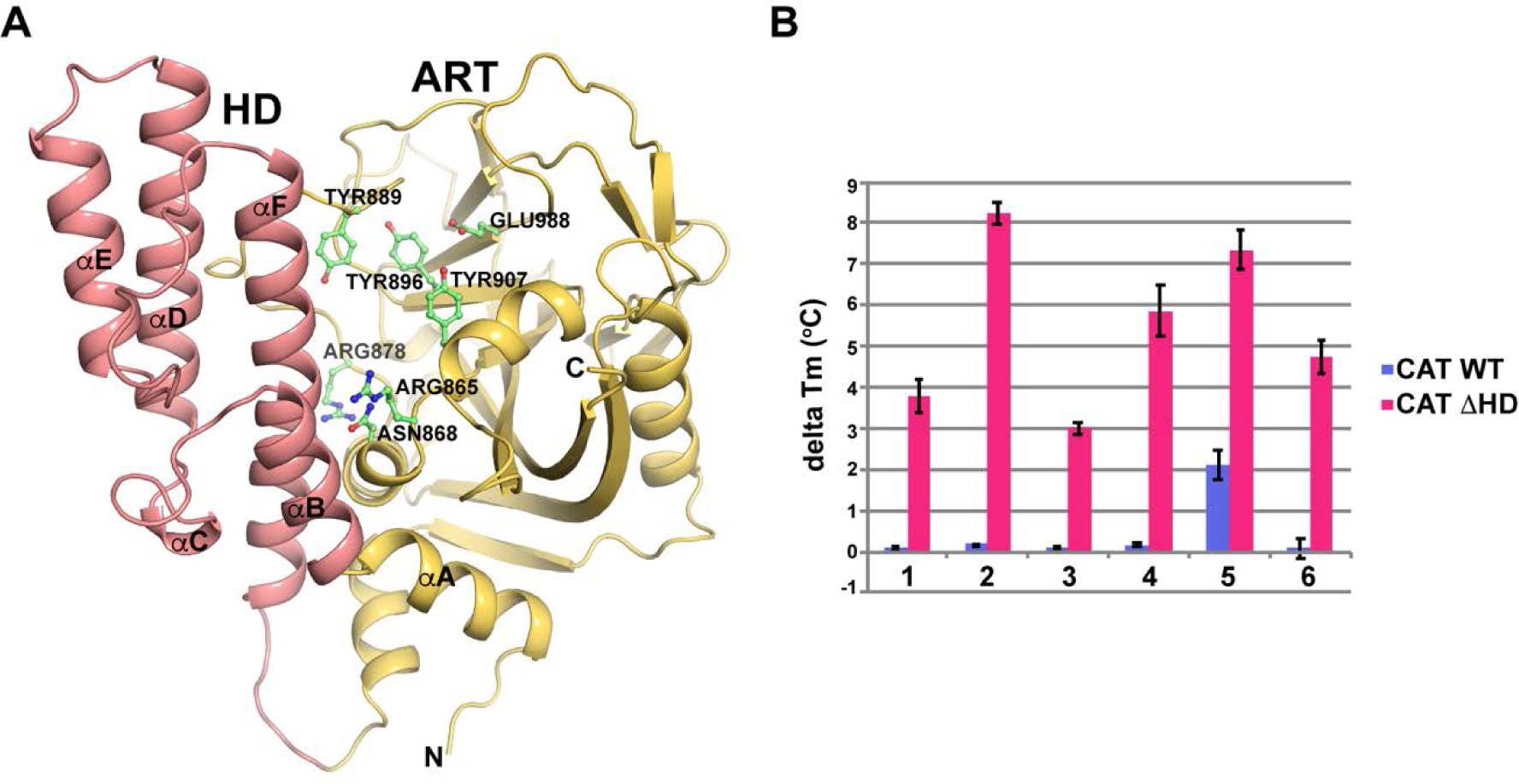
Inhibitor binding to the PARP-1 catalytic domain. (A) Ribbon representation of the PARP-1 catalytic domain (CAT) using PDB code 3gjw.71 The HD and ART domains are indicated in red and orange, respectively. Several residues are labeled and numbered, and the N-terminus (labelled as N) and C-terminus (labelled as C) are noted. (B) DSF was used to assess the capacity of inhibitors to bind to the catalytic domain of PARP-1 (CAT), or the catalytic domain with the HD deleted (CATΔHD). The change in melting temperature (delta TM) of PARP-1 CAT and CATΔHD in the presence of the indicated PARP inhibitors was measured. The delta TM was calculated by subtracting the TM values of CAT or CATΔHD alone from the values obtained in the presence of inhibitor. The averages of three experiments are shown, and the error bars represent the standard deviations. Note: (1) pyrimidinyl piperazine analogue 63; (2) tetrazolyl analogue 57; (3) benzimidazole-2-yl-ethylamine analogue 93; (4) cyclopropyl THTP analogue 83; (5) benzimidazole-2-yl-piperazine analogue 103; (6) benzamide adenine dinucleotide.
