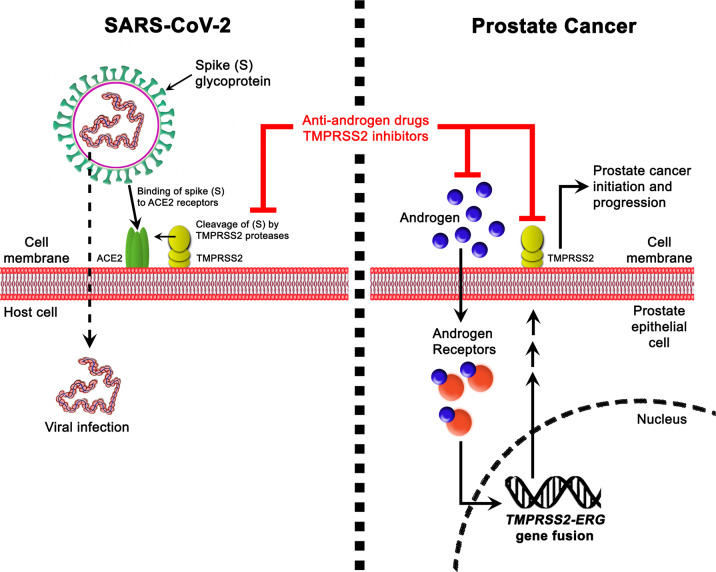
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the crosstalk between COVID-19 and prostate cancer.
Potential association is present between SARS-CoV-2 targets on host epithelial cells on one hand, and prostate cancer genetic aberrations and molecular signatures, such as AR and TMPRSS2, on the other hand. Antiandrogen drugs and TMPRSS2 inhibitors used in prostate cancer might hence serve as common therapeutic options for COVID-19 patients.