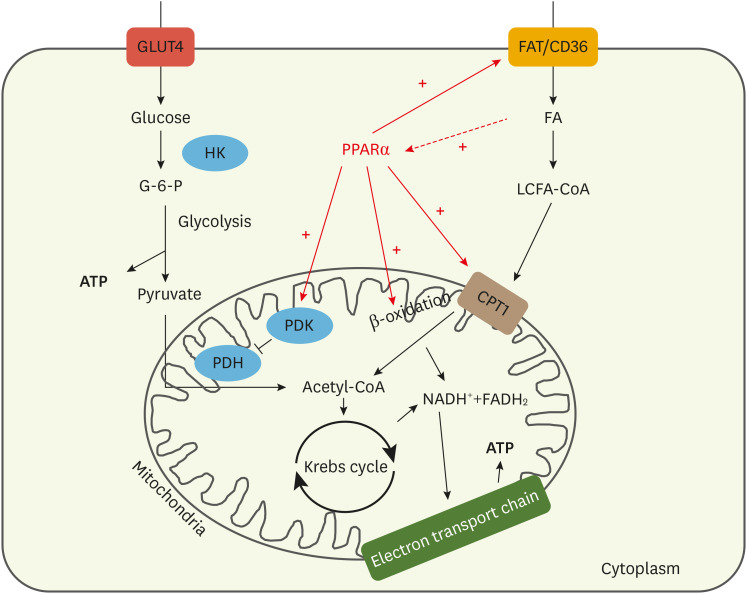
Fig. 3. Schematic representing changes mediated by PPARα, which is upregulated in the diabetic heart. Upon FA binding, PPARα becomes activated and dimerises with the retinoic acid receptor. This heterodimer can then bind to the PPAR response element and activate a plethora of genes. This includes genes involved in FA uptake, mitochondrial FA uptake and β-oxidation, including fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD36) and CPT1. Furthermore, PPARα also promotes upregulation of PDK, inhibiting PDH and reducing glycolytic flux.
PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; FA, fatty acids; CPT1, carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1; PDK, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; HK, hexokinase; G-6-P, glucose-6-phosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; LCFA-CoA, long chain fatty acyl coenzyme A.