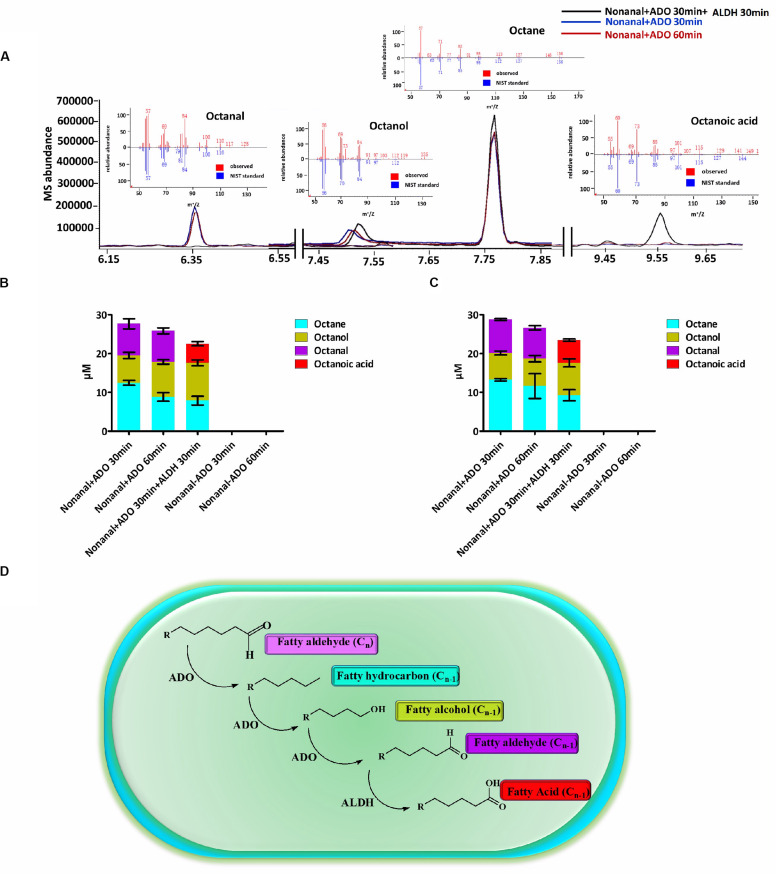
FIGURE 1.
A cyanobacterial ADO-ALDH alka(e)ne biodegradation pathway was identified by in vitro enzymatic assays. (A) GC-MS chromatograms of Syn7942 ADO-ALDH reaction with nonanal as the substrate. The inset shows the mass spectra of octane, octanal, octanol, and octanoic acid from GC-MS analysis (red) compared with mass spectra from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) database (blue). (B) Product profiles of the Syn7942 ADO-ALDH reaction with nonanal as the substrate. (C) Product profiles of the Nos73102 ADO-ALDH reaction with nonanal as the substrate. (D) Proposed mechanism for the cyanobacterial ADO-ALDH alka(e)ne degradation pathway. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of triplicate analyses.