Figure 4.
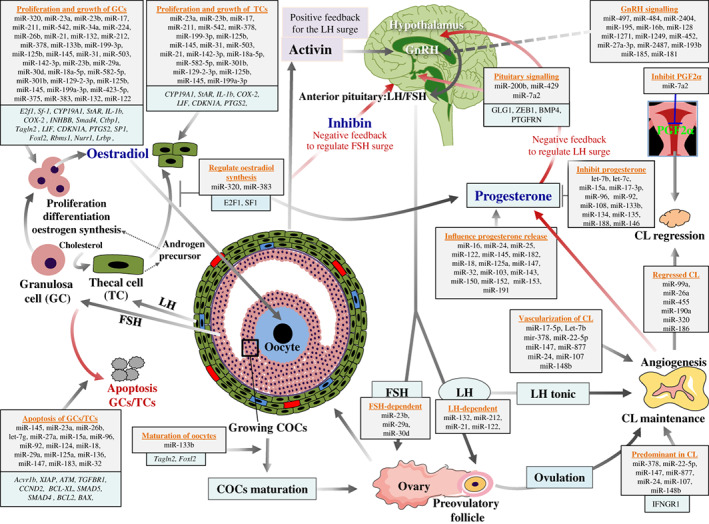
MicroRNA (miRNA) regulation in the maintenance of female hormonal balance. The proliferation, growth, differentiation, functioning, and apoptosis of female steroidogenic cells [granulosa cell (GC) and thecal cell (TC)] are highly regulated by miRNAs. miRNAs are also active regulators of female steroidogenic genes including cytochrome P450 family 19 subfamily A member 1 (Cyp19a1); steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (Star), and prostaglandin‐endoperoxide synthase 2 (Ptgs2); thus, miRNAs directly regulate the steroidogenic process in females through gonadotropin‐releasing hormone (GnRH), follicle‐stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH) signalling. The vasculogenesis and angiogenesis of progesterone‐producing corpus lutem (CL) is also related to the expression of miRNAs, making miRNAs important regulatory molecules during the female steroidogenic processes. miRNAs are involved in both follicular steroidogenesis and luteal steroidogenesis. PGF2α, prostaglandin; COC, cumulus‐oocyte complex; E2f1, E2F transcription factor 1; Sf‐1, steroidogenic factor 1 nuclear receptor; IL‐1b, interleukin 1 beta; COX‐2, cyclooxygenase 2; INHBB, inhibin beta B subunit; Ctbp1, C‐terminal binding protein 1; Tagln2, transgelin 2; LIF, leukemia inhibitory factor; CDKN1A, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; SP1, specificity protein 1; Foxl2, forkhead box L2; Rbms1, RNA binding motif single stranded interacting protein 1; Nurr1, nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2; Lrbp, LH receptor mRNA‐binding protein; Acvr1b, activin A receptor type 1B; XIAP, X‐linked inhibitor of apoptosis; ATM, ATM serine/threonine kinase; TGFBR1, transforming growth factor beta receptor 1; CCND2, cyclin D2; BCL‐XL, BCL2 like 1; SMAD5, SMAD family member 5; SMAD4, SMAD family member 4; BCL2, B‐cell lymphoma 2; BAX, BCL2 associated X protein; GLG1, Golgi glycoprotein 1; ZEB1, zinc finger E‐box binding homeobox 1; BMP4, bone morphogenetic protein 4; PTGFRN, prostaglandin F2 receptor inhibitor; IFNGR1, interferon gamma receptor 1.
