Figure 1.
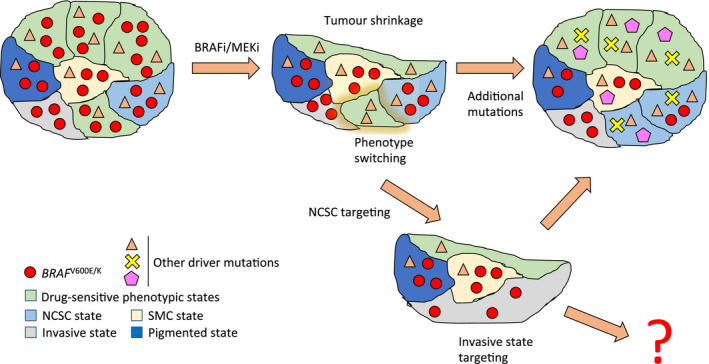
Both mutational and non‐mutational mechanisms for the acquisition of drug resistance can be operational in a tumour. A tumour with BRAF V600E/K mutations is treated with BRAFi/MEKi. The BRAF‐mutated cells in drug‐sensitive phenotypic states die, but cells in the four drug‐tolerant phenotypic states survive treatment. Cells can also undergo phenotype switching to the NCSC state that ultimately gives rise to relapse. Then, additional somatic mutations can be acquired that allow the tumour to grow and resist treatment. If the NCSC subpopulation is targeted, the tumour takes significantly longer to relapse, but eventually does so upon expansion of cells in the “invasive” state. The invasive state could also potentially be targeted. Note that this diagram is over simplistic and that different subpopulations can co‐exist in the same geographical space. NCSC: Neural crest stem cell‐like, SMC: starved‐like melanoma cells
