Figure 3.
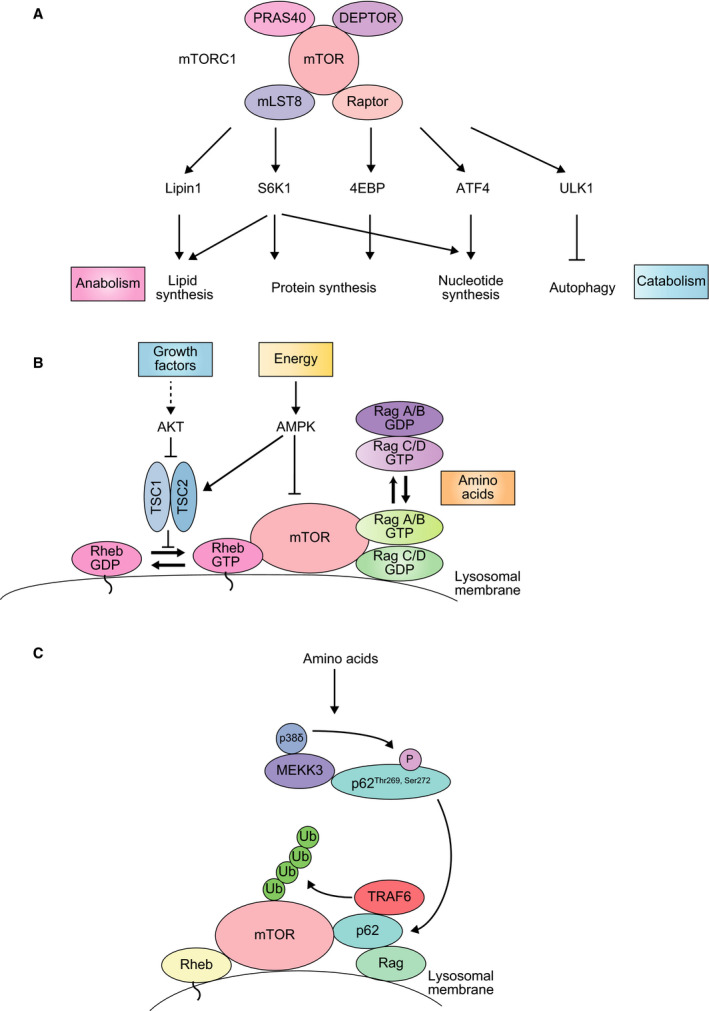
(A) The mTORC1 pathway. The mTORC1 complex is formed by the mTOR kinase, the regulator subunits Raptor and PRAS40 and the inhibitors mLST8 and DEPTOR. Upon mTORC1 stimulation, downstream effectors promote anabolism and suppress catabolism. (B) The activity of mTORC1 is inhibited by the TSC complex, which is itself inactivated in the presence of growth factors and upregulated upon energy deprivation. In the later situation, AMPK inhibits mTORC1 both directly and through TSC activation. Increased amino acid availability converts RagA/B GDP and RagC/D GTP into RagA/B GTP and RagC/D GDP respectively, assembling mTORC1 on the lysosome, where Rheb activates mTORC1. (C) mTORC1 activation by p62. Amino acid stimulation promotes the phosphorylation of p62 at Thr269 and Ser272 by MEKK3/p38delta. This results in the formation of a signaling hub over the lysosomal membrane through the interaction of p62 with Raptor, TRAF6 and Rag proteins. As a consequence, mTOR is ubiquitinated by TRAF6, and then activated by Rheb.
