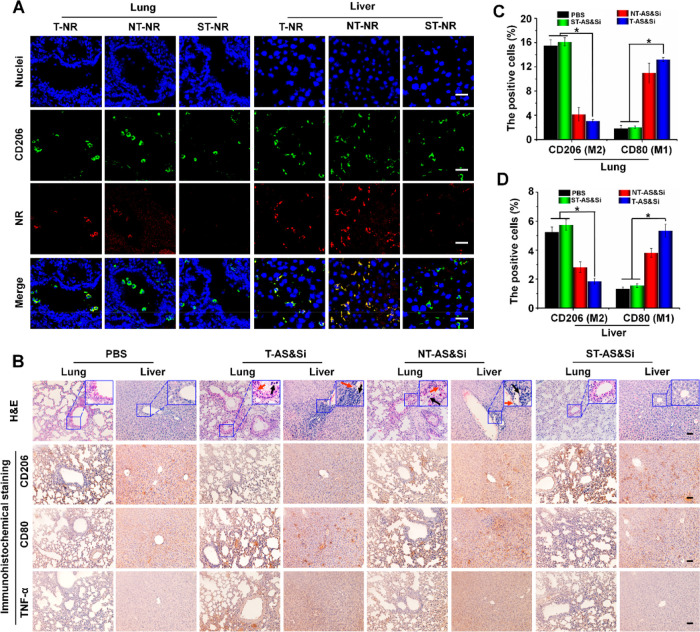
Figure 7.
Decreased proinflammatory effects in the liver and lung via tumor acidity-triggered targeting delivery. (A) Confocal laser scanning microscopic (CLSM) imaging showing uptake of micelleplex T-NR, NT-NR, or ST-NR by M2-like macrophages in the lung and liver after 24 h postinjection of the micelleplex. Green fluorescence indicates anti-CD206 antibody labeling M2 macrophages, and red fluorescence indicates NR-loaded micelles. Scale bars represent 25 μm. (B) H&E staining and immunohistochemical assay of the lung and liver from mice after receiving treatments of PBS, T-AS&Si, NT-AS&Si, or ST-AS&Si every 2 days for a total of five injections. Red arrows indicate damages of the alveolar wall in lung and hepatic sinusoid well in the liver, and black arrows show inflammatory cells. Amounts of M2- or M1-like macrophages and expressions of M1-associated proinflammatory factor TNF-α in the lung and liver were analyzed by immunohistochemical assay to explore the inflammatory reaction. CD206-positive cells (M2) and CD80-positive cells (M1) counted in the lung (C) and liver (D), *P < 0.05. Scale bars represent 50 μm; siRNA dose, 250 μg/kg body weight; AS dose, 60 μg/kg body weight.