Figure 3.
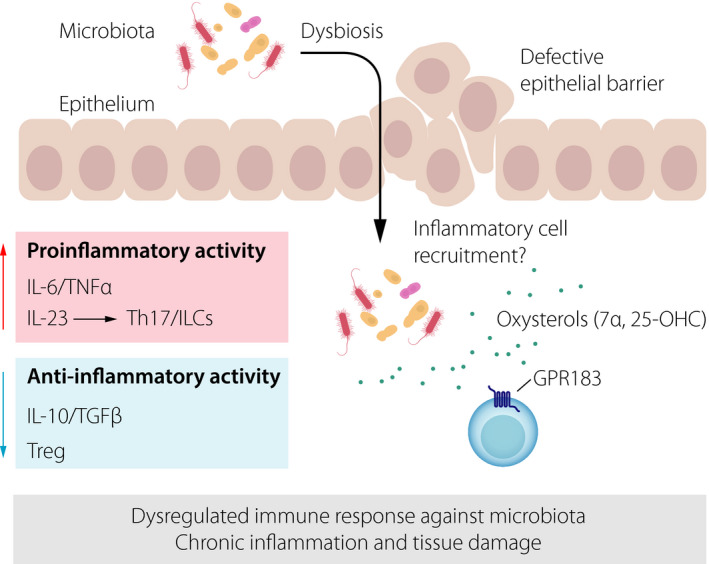
Key mechanism of intestinal inflammation. Defective epithelial barrier function combined with dysbiosis stimulates pro‐inflammatory immune activity, whilst anti‐inflammatory pathways are impaired. This leads to a dysregulated immune response against the host's microbiota, thereby causing chronic inflammation and tissue damage. The possible role of oxysterols (sensed through the receptor GPR183 on immune cells) in promoting inflammatory cell recruitment is shown.
