Figure 6.
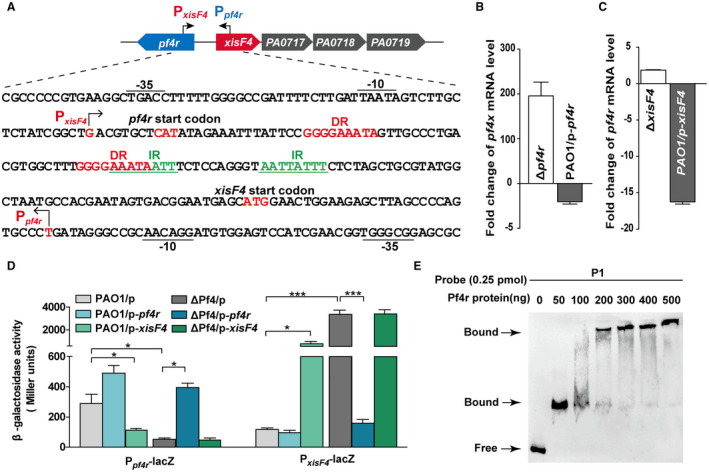
Pf4r represses xisF4 while activating itself. A. A schematic diagram indicates the intergenic region between xisF4 and xisF5. The transcriptional start sites of xisF4 and pf4r were determined by 5′‐RACE, and arrows indicate the direction of transcription. DR and IR indicate directed and inverted repeats, respectively. B. Fold change of mRNA levels of xisF4 in Δpf4r versus PAO1, and in PAO1/pHERD20T‐pf4r versus PAO1/pHERD20T. C. Fold change of mRNA levels of pf4r in ΔxisF4 versus PAO1, and in PAO1/pHERD20T‐xisF4 versus PAO1/pHERD20T. D. The β‐galactosidase activity of Ppf4r – lacZ and PxisF4 – lacZ were determined in PAO1 and ΔPf4 carrying pHERD20T, pHERD20T‐pf4r and pHERD20T‐xisF4, respectively. 10 mM arabinose was added for induction for 3 h at OD600 ~ 0.1. Three independent cultures of each strain were used, and error bars indicate standard deviation in B, C and D. E. EMSA showed that Pf4r bound to the promoter region of P1 (as shown in Fig. A) in a concentration‐dependent manner.
