Figure 7.
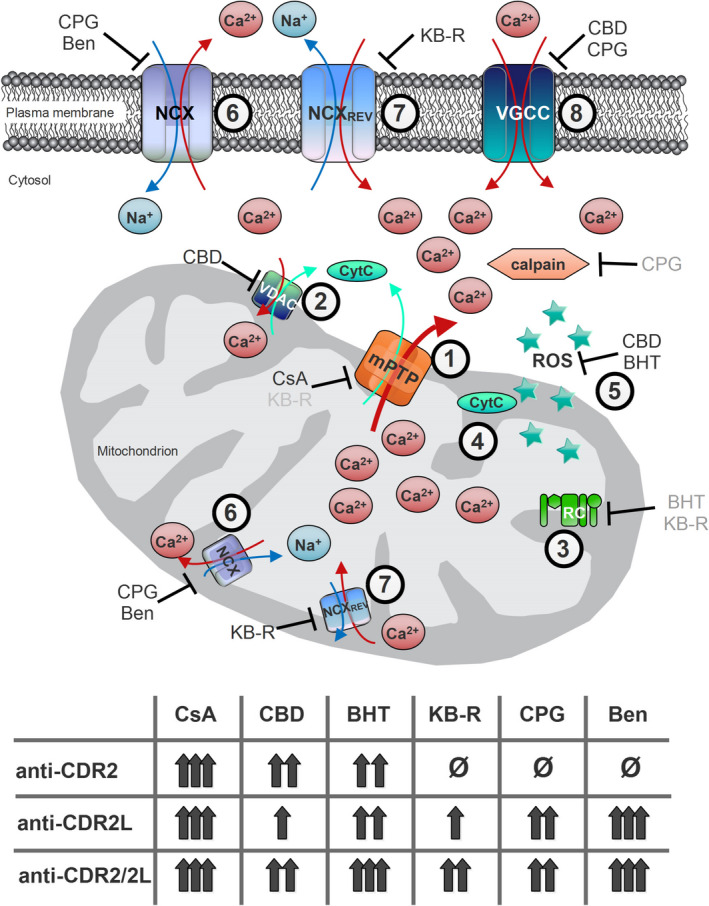
Calcium flux regulation in Purkinje neurons. Schematic diagram illustrates important calcium flux regulators in Purkinje neurone calcium homeostasis and how the six used antagonists modulate calcium flux and reveal neuroprotective capacity in antibody‐dependent manner. Some of the used antagonists have multiple targets, and a total of eight calcium flux regulating processes were subdue: (1) mitochondria permeability transition pore opening by cyclosporin‐A (cyclophilin D‐dependent) and KB‐R7943 (cyclophilin D‐independent, grey), (2) voltage‐dependent anion channels (VDAC) activity by cannabidiol (CBD), (3) respiratory chain (RC) regulation indirectly by butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) and KB‐R7943 (grey), (4) cytochrome‐c (Cyt C) production by CBD, (5) reactive oxygen species production by BHT and CBD, (6) Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) activity by CGP37157 and benzamil, (7) NCX rev activity by KB‐R7943 and (8) voltage‐gated calcium channels (VGCC) activity by CGP37157 and CBD. Balancing these eight calcium‐sensitive targets resulted in moderate (single arrow) to high (triple arrows) neuroprotective effects during anti‐Yo/rCDR internalization, with one exception. In Purkinje neurone degeneration caused by anti‐rCDR2, inhibition of NCX (process 6) or its reverse mode (process 7) showed no beneficial effect (ø). Indirect inhibitory effects are marked in grey.
