Figure 1.
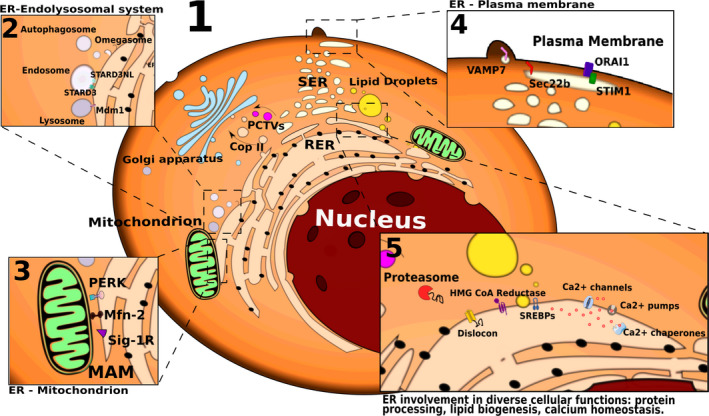
ER molecular machines and contact sites with other organelles. The ER is primarily subdivided into the SER and RER, with the latter characterized by the presence of ribosomes at its cytosolic surface. Alternatively, the ER has been recently classified into the nuclear envelope, ER sheet‐like cisternae and tubular ER (panel 1). The ER forms multiple membrane contact sites with other organelles, including the endosomes and lysosomes (through STARD3, STARD3NL, Mdm1; panel 2), the mitochondria (through Mfn‐2, Sig‐1R, PERK; panel 3), and the PM (through ORAI1, STIM1, Sec22b, VAMP7; panel 4) with various functional implications. The ER plays instrumental roles in secretory and transmembrane protein folding and quality control, protein and lipid trafficking, lipid metabolism, and Ca2+ homeostasis, all of these processes being mediated by a diverse series of ER resident proteins (schematically depicted in panels 1 and 5).
