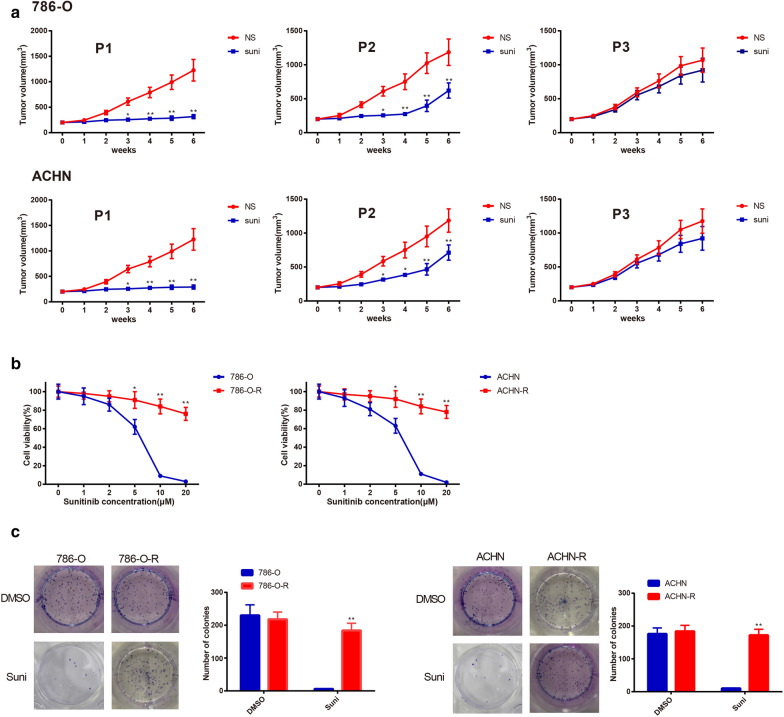
Fig. 1.
Establishment of cell line resistant to sunitinib. Tumor size was recorded after nude mice were injected with 786-O, ACHN, first-generation or second-generation tumor cells. The tumor cells in the third-generation were found to resistant to sunitinib (a). The reactions of parental cells (786-O and ACHN) and sunitinib-resistant cells (786-O-R and ACHN-R) to sunitinib were measured by CCK-8 assay. High concentration of sunitinib significantly inhibited the activity of 786-O and ACHN cells (b). Colony formation assay was employed to count the clone number of parental cells and sunitinib-resistant cells after 10 μM of sunitinib or DMSO treatment. Sunitinib at 10 μM markedly repressed the formation of parental cell clones, but had no effect on sunitinib-resistant cells (c). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared to NS or 786-O or ACHN group; DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide; NS, normal saline