Figure 5.
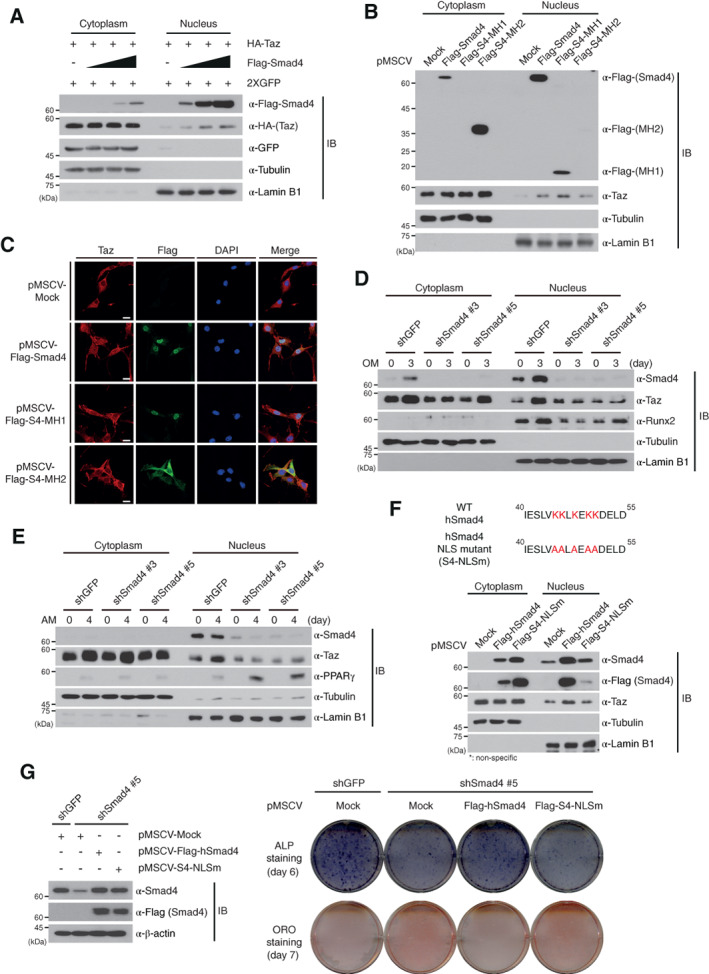
Smad4 induces nuclear localization of Taz. (A, B): A plasmid encoding HA‐Taz was cotransfected with dose‐dependent increases of the Flag‐Smad4 plasmid into HEK293 cells, which were subsequently fractionated (A). Stable C3H10T1/2 cells expressing the indicated plasmids were fractionated into cytoplasm and nuclei. The localization of Taz was analyzed by IBs with the indicated antibodies. The empty vector, pMSCV, was used as a negative control in (B) (Mock). (C): Localization of endogenous Taz in stable C3H10T1/2 cells expressing the indicated plasmids was detected by immunofluorescence analysis. The empty vector, pMSCV, was used as a negative control (Mock). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 μm. (D, E): Smad4‐knockdown and shGFP‐expressing C3H10T1/2 cells in osteogenic (D) or adipogenic (E) differentiation medium were fractionated on day 3 or day 4, respectively, and the Taz localization was analyzed by immunoblotting. (F): Stable C3H10T1/2 cells expressing wild‐type human Smad4 (Flag‐hSmad4) and Smad4 NLS mutant (Flag‐S4‐NLSm) were fractionated and the localization of Taz was detected by immunoblotting. (G): Ectopic expression of Flag‐hSmad4 or Flag‐S4‐NLSm in Smad4‐knockdown C3H10T1/2 cells was detected by IB analysis (left). β‐actin expression was used as a loading control in IBs. Osteogenesis and adipogenesis of Smad4‐knockdown cells ectopically expressing Flag‐hSmad4 or Flag‐S4‐NLSm were observed at the indicated time points with ALP or ORO staining. The empty vector, pMSCV (Mock). The images in this figure are representative of three independent experiments. Expressions of α‐tubulin and α‐Lamin B1 in (A), (B), and (D)–(F) were used as cytoplasmic and nuclear markers and loading controls. Abbreviations: ALP, alkaline phosphatase; DAPI, 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IB, immunoblot; NLS, nuclear localization signal; OM, osteogenic differentiation medium; ORO, oil red O; Runx2, runt‐related transcription factor 2; shGFP, green fluorescent protein‐specific short hairpin RNA.
