Extended Data Fig. 10 |. HVC neurons can be tuned to complementary preceding contexts.
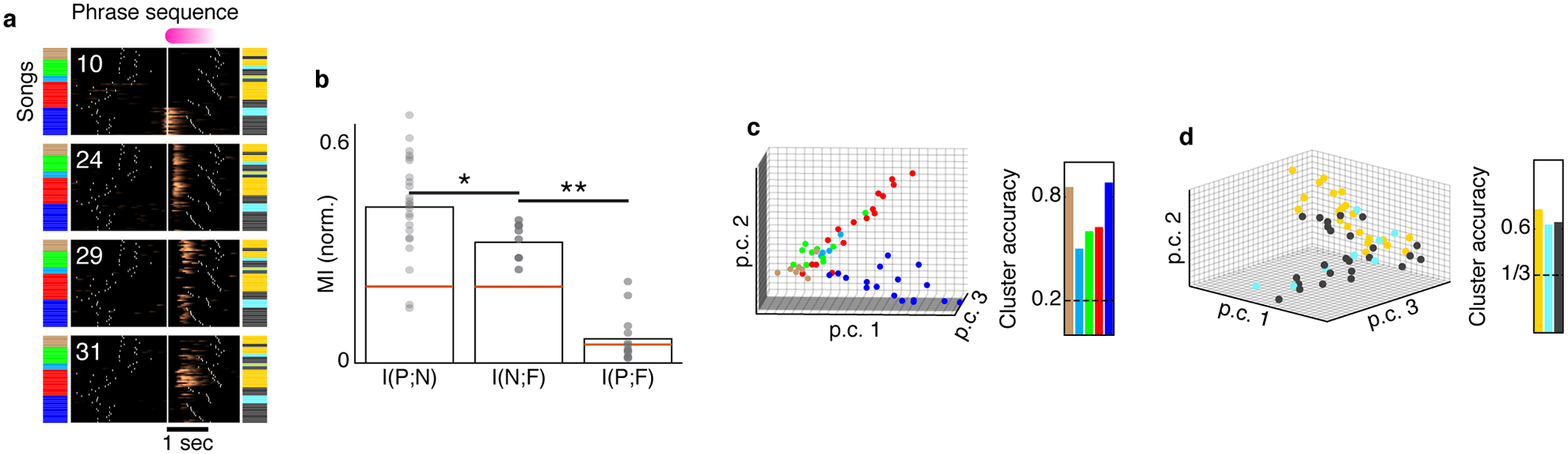
a. Four jointly-recorded ROIs exhibit complementary context selectivity. Color bars indicate phrase identities preceding and following a fixed phrase (pink). For each ROI (rasters), (Δf/f0)denoised traces are aligned to the onset of the pink phrase (x-axis) arranged by the identity of the preceding phrase, by the following phrase and finally by the duration of pink phrase. b. For the example in (a), normalized mutual information between the identity of past (P) and future (F) phrase types is significantly smaller than the information held by the network states about the past and future contexts (left bars. N is the 4-ROIs activity). Dots, bars, and red lines mark bootstrap assessment shuffles, their mean, and the 95% level of the mean in shuffled data (methods). *: difference is 0.09 ± 0.03, Z =4.3, p=7.3e-6, **: difference is 0.26 ± 0.02, Z=8.9, p< 1e-15, bootstrapped one-sided z-test. c. Signal integrals from the 4 ROIs in panel a are plotted for each song (dots, N=54 songs) on the 3 most informative principle components. Dots are colored by the identity of the preceding phrase. Clustering accuracy measures the ‘leave-one-out’ label prediction for each preceding phrase (true positive), calculated by assigning each dot to the nearest centroid (L2). Dashed line marks chance level. d. Similar to panel c but for the 1st following phrase.
