Figure 4 |. Sequence-correlated HVC neurons reflect preceding context up to four phrases apart and show enhanced activity during context-dependent transitions.
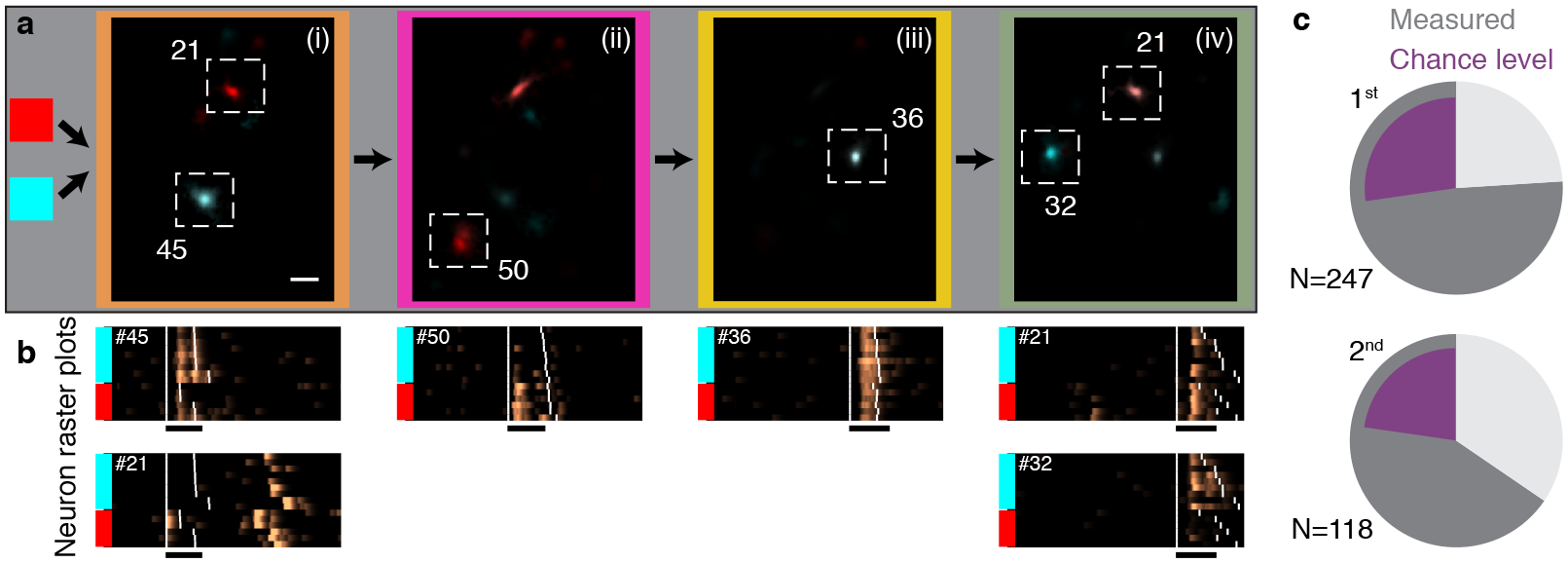
a. A sequence of four phrases (i-iv, color coded) is preceded by two upstream phrase types (red or cyan). Average maximum projection denoised images (methods) are calculated in each sequence context during each phrase in the sequence (i-iv) and overlaid in complementary colors (red, cyan) to reveal context-preferring neurons. Scale bar is 50 μm. b. (Δf/f0)denoised rasters for the ROIs in panel (a). Songs are ordered by the preceding phrase type (colored bars). Extended Data Fig. 8a shows the statistical significance of song context relations. c. Fraction of sequence-correlated ROIs found in complex transitions. Pie charts separate 1st order and higher order (≥2nd) sequence correlations. Dark grey summarizes the total fraction for two birds. Purple shows fractions expected from sequence correlates uniformly-distributed in all phrase types.
