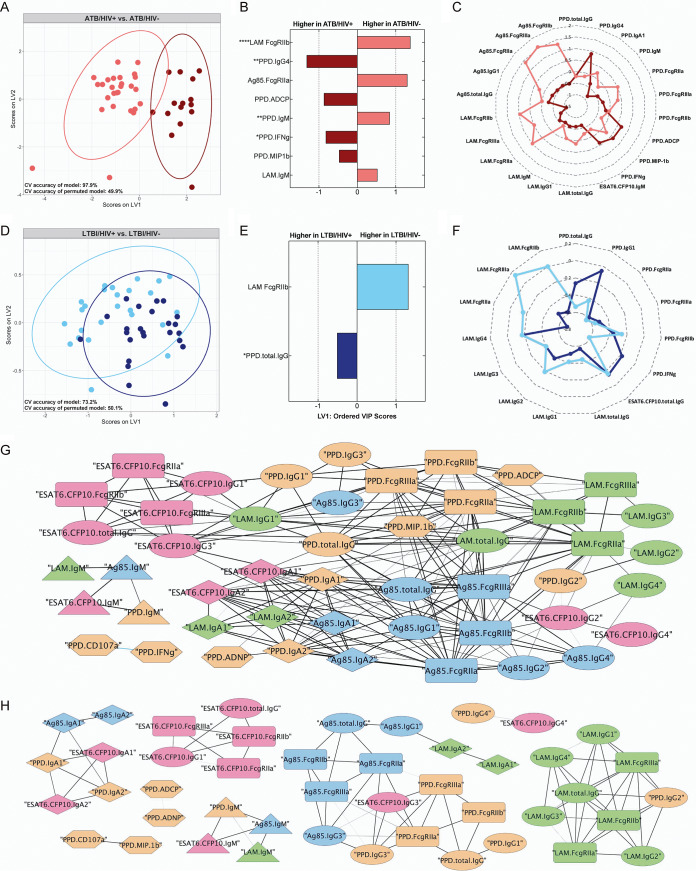
FIG 5.
HIV-positive and HIV-negative M. tuberculosis-infected individuals exhibit divergent M. tuberculosis-specific humoral profiles. Multivariate analyses comparing M. tuberculosis-specific antibody responses elicited by HIV-positive and HIV-negative individuals. (A and D) Visualization from PLS-DA models trained using the LASSO-selected features in the ATB (A) and LTBI (D) subset of individuals. Ellipses represent 95% confidence intervals. Cross validation (CV) accuracy of the models and permuted models are indicated. The accuracy of each model is significantly higher than that of the respective permuted model (Mann-Whitney U test ATB model, P < 2.2e−16; Mann-Whitney U test LTBI model, P < 2.2e−16). (B and E) LASSO-selected features from the ATB (B) and LTBI models (E) are plotted on variable importance in the projection (VIP) plots. Variables with VIP scores greater than 1 contribute most to separation across latent variable 1 (LV1). LASSO-selected features significantly different across the groups during univariate analyses are indicated. Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple-comparison test was used. Adjusted P values are as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. (C and F) Radar plots of each LASSO-selected feature and its significant correlates in the ATB (C) and LTBI (F) models. Median Z-score of each group is plotted for a given feature. (G and H) Correlation networks depict significant correlations within the M. tuberculosis-specific antibody response in HIV-negative (G) and HIV-positive (H) individuals. LTBI and ATB individuals were combined to make each correlation network. The width of each edge corresponds to the magnitude of the Spearman r values. Colors: orange (PPD), green (LAM), blue (Ag85A/B), pink (ESAT6/CFP10). Shapes: ellipse (IgG titer), diamond (IgA titer), triangle (IgM titer), rounded rectangle (Fc-receptor binding), hexagon (functional assay). Significant correlations were defined as those with q value of <0.01. The q values were calculated using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure (77).