FIG 4.
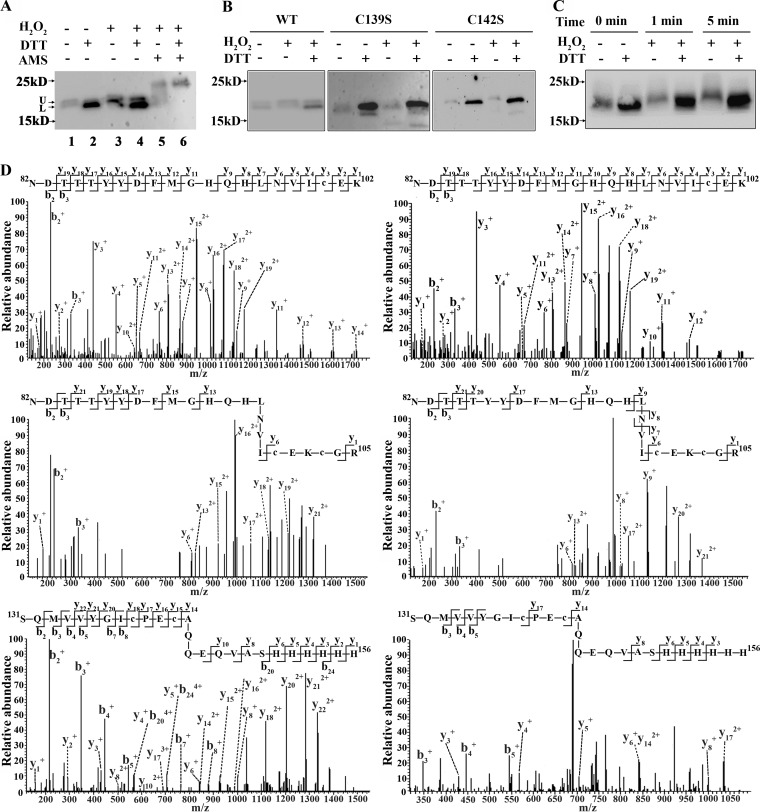
Assay of PerR cysteine oxidation in 40 μM H2O2-treated cells. (A) A 6×His tag was fused to the C terminus of perR (KEGG accession number I872_05555) to construct the S. oligofermentans PerR-6×His strain. Using the same approach described in the legends to Fig. 3A and B, redox Western blotting detected cysteine oxidation in the 6×His-tagged PerR protein using the anti-His tag antibody. U and L at the gel left indicate upper and lower protein bands, respectively. (B) A serine substitution of either Cys139 or Cys142 was constructed on a shuttle plasmid (pDL278-perR-6×His), and the plasmid was transformed into the perR deletion strain to construct the perR::pDL278-perRC139S-6×His (C139S) and perR::pDL278-perRC142S-6×His (C142S) strains. The perR deletion mutant harboring pDL278-perR-6×His (WT) was included as a control. The three strains were anaerobically cultured and then treated with 40 μM H2O2. Redox Western blotting, as described in the legend to Fig. 3A, was carried out to detect the oxidation of the PerR mutants. (C) The PerR-6×His strain was anaerobically cultured, and cells were treated with 40 μM H2O2 for 1 min and 5 min. Using the methods described in the legend to Fig. 3A, the cysteine oxidation of PerR was detected by redox Western blotting. (D) The 6×His-tagged PerR protein was immunoprecipitated from the statically grown PerR-6×His strain as described in Materials and Methods and then resolved on an 18% nonreducing SDS-PAGE gel. The protein band was then subjected to differential alkylation and LC-MS/MS analysis. (Top) Representative MS/MS spectra of the triply charged peptide ions at m/z 863.7217 and 862.7243, corresponding to reduced (left) and oxidized (right) NDTTTYYDFMGHQHLNVIC100EK peptide fragments, respectively. (Middle) Representative MS/MS spectra of triply charged peptide ions at m/z 989.1003 and 992.4445, corresponding to both Cys100 and Cys103 reduced (left) and oxidized (right) NDTTTYYDFMGHQHLNVIC100EKC103GR peptide fragments, respectively. (Bottom) The MS/MS spectra represent triple- and quintuple-charged peptide ions at m/z 1038.1281 and 622.0834, respectively, corresponding to both Cys139 and Cys142 reduced (left) and oxidized (right) SQMVVYGIC139PEC142AQQEQVASHHHHHH peptide fragments. The reduced and oxidized cysteine residues were 13C carboxymethylated and 12C carbamidomethylated, respectively.