Figure 7.
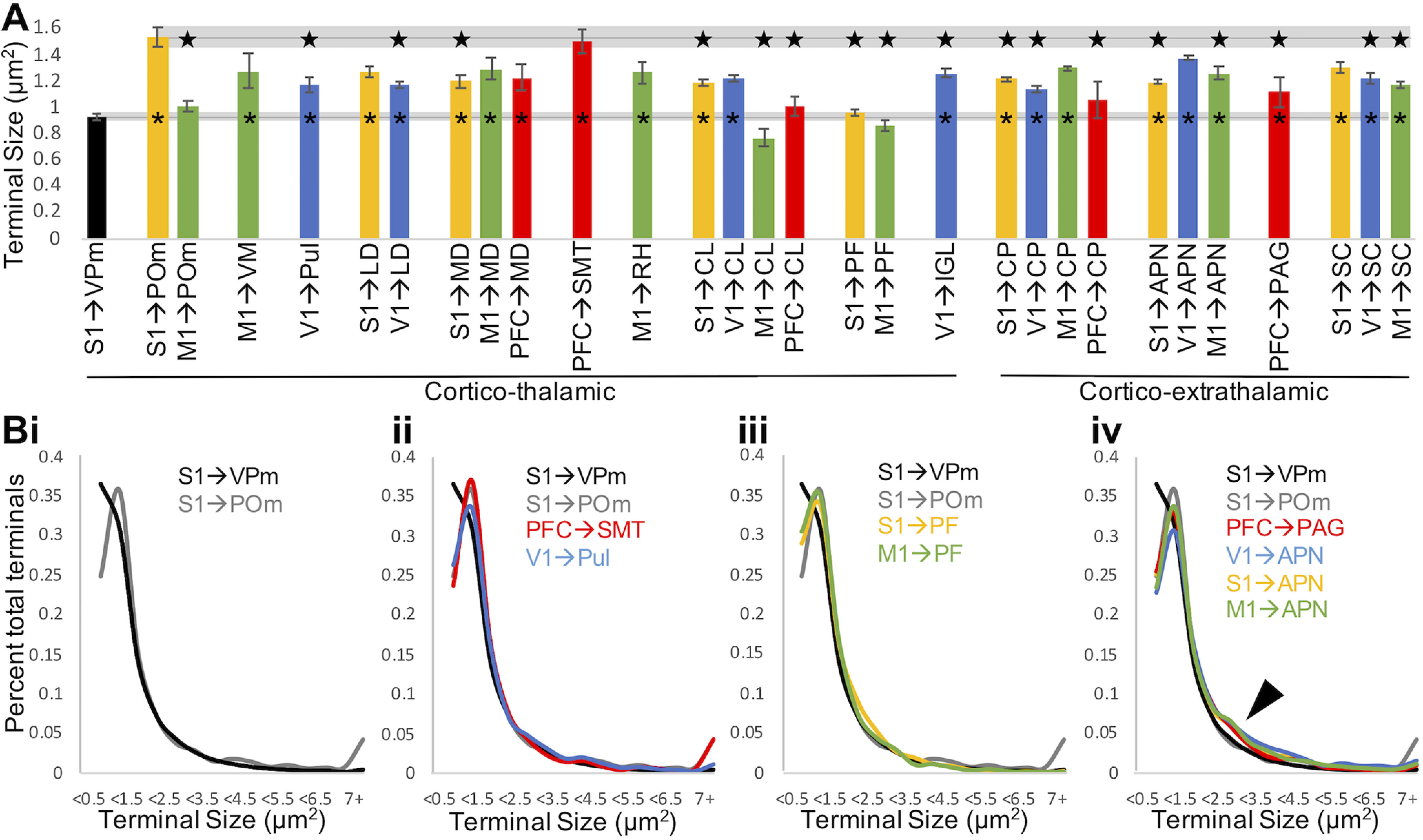
L5 terminal size is pathway-specific. A, For a given pathway, bars represent mean terminal size and error bars indicate SEM among animals (n = 2-4 per group). For most pathways, average terminal size falls between the small and large terminals established in mouse somatosensory thalamus. The average terminal size in the ventral posteromedial nucleus of Rbp4-Cre negative mice and in the posterior medial nucleus of Cre+ mice is shown to the left and extended across the graph for easy comparison with these previously established small and large populations. *p < 0.001, significant difference from terminals in the ventral posteromedial nucleus (ANOVA with animal and pathway as between-subjects variables, Tukey HSD post hoc test). Star represents significant difference (p < 0.001) from terminals in the posterior medial nucleus (ANOVA with animal and pathway as between-subjects variables, Tukey HSD post hoc test). B, Population distributions of terminal size for pathways of interest. Bi, S1 terminals in the posterior medial nucleus exhibit fewer small and more large terminals than in the posterior medial nucleus. Bii, PFC terminals in submedial nucleus and V1 terminals in the pulvinar exhibit a terminal size distribution similar to S1 terminals in posterior medial nucleus. Biii, S1 and M1 terminals in the parafascicular nucleus exhibit a distribution of small terminals similar to the posterior medial nucleus but, similar to the ventral posteromedial nucleus, lack large terminals. Biv, Terminals in example extrathalamic pathways exhibit more terminals of intermediate size (arrowhead). APN, Anterior prectectal nucleus; CL, central lateral nucleus; CP, caudoputamen; IGL, intergeniculate leaflet; LD, lateral dorsal nucleus; MD, mediodorsal nucleus; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PF, parafascicular nucleus; POm, posterior medial nucleus; Pul, pulvinar; RH, rhomboid nucleus; SC, superior colliculus; SMT, submedial nucleus; VM, ventral medial nucleus; VPm, ventral posteromedial nucleus.
