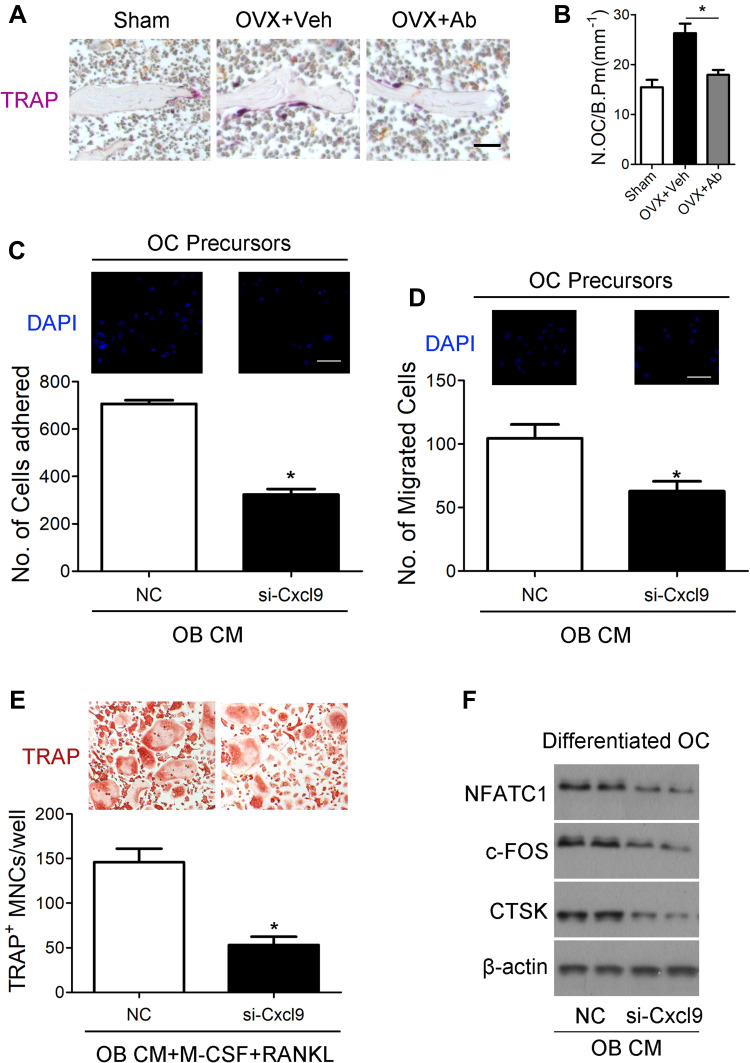
Figure 4.
Cxcl9 facilitates bone resorption in vivo and in vitro. (A) TRAP staining of tibia sections from OVX mice treated with vehicle or Cxcl9–neutralizing antibody (Anti-Cxcl9) with the first injection at the same day of OVX. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) The number of osteoclasts (N.OC) on bone surface (/B.Pm) was measured. (C) Osteoclast precursors (Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages (BMM)) were treated with 50 ng/mL M-CSF for 60 hours. Cells were incubated for 10 minutes on fibronectin-coated culture plates supplemented with the indicated conditional medium from osteoblasts (OB CM) pretreated with Cxcl9 siRNA (si-Cxcl9) or negative control (NC). Nonadherent cells were washed with PBS, and adherent cells were stained with DAPI and counted under a fluorescence microscope. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Osteoclast precursors were cultured in the presence 50 ng/mL M-CSF plus 100 ng/mL RANKL for 60 hours. Cells were washed with PBS, suspended in serum-free α-MEM, and loaded to the upper well of transwell chambers. The lower well contained conditional medium from osteoblasts (OB CM) pretreated with Cxcl9 siRNA (si-Cxcl9) or negative control (NC). After 6 hours, cells migrated onto the lower well were stained with DAPI and counted under a fluorescence microscope. Scale bar, 50 μm. (E) BMMs were incubated with conditional medium from osteoblasts (OB CM) pretreated with Cxcl9 siRNA (si-Cxcl9) or negative control (NC) with supplementary M-CSF and RANKL. After 72 h, osteoclast formation was analyzed by TRAP staining and numbers of osteoclasts were counted as TRAP-positive multinucleated cells (TRAP+ MNCs). (F) Immunoblotting was carried out to detect expression of osteoclast markers in the differentiated BMMs. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. *P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test).